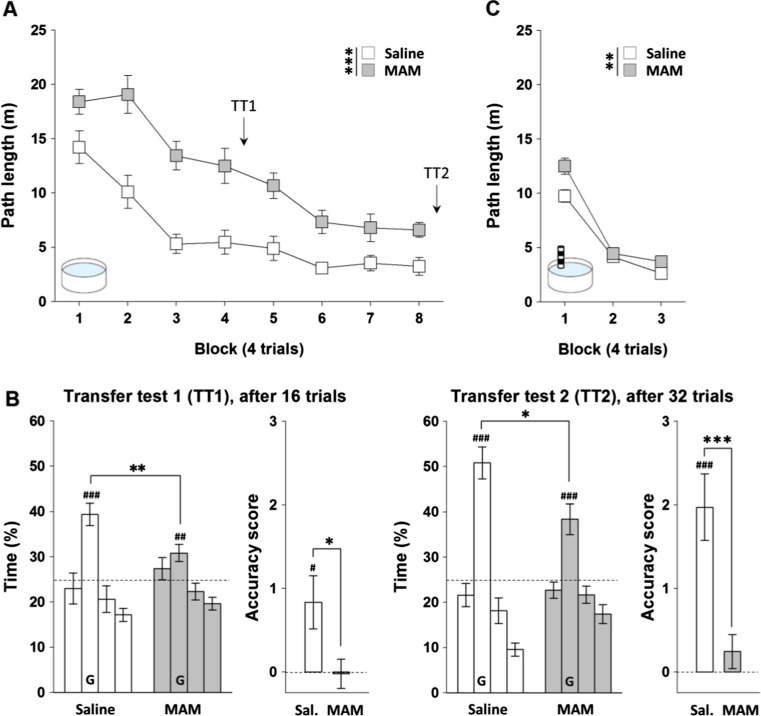
Fig. 2.
MAM E17 exposure impaired both hidden (a–b) and visible platform learning (c) in the aversively motivated Morris watermaze. Hidden and visible platform Morris watermaze learning tasks were assessed in a separate laboratory (Oxford University in collaboration with Eli Lilly, UK) and in two separate cohorts of rats. a Results from the hidden platform learning task are presented as the mean ± SEM of the path lengths travelled to reach the platform across each of the four-trial training blocks for both MAM E17 rats (grey, n = 15) and saline controls (white, n = 12). b Transfer tests were conducted 24 h after the fourth (TT1) and eighth (TT2) block of training. Results are presented as the mean ± SEM of the percentage of time spent in the goal quadrant (G) and other three quadrants, as well as the platform crossing accuracy score for each transfer test. Dashed lines represent 25 % chance level. c Results from the visible platform learning task are presented as the mean ± SEM of the path lengths travelled to reach the platform across each of the four-trial training blocks for MAM E17 rats (grey, n = 16) and saline controls (white, n = 13). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 vs. the saline-treated group. # P < 0.05; ## P < 0.01; ### P < 0.001 vs. chance level