Figure 1.
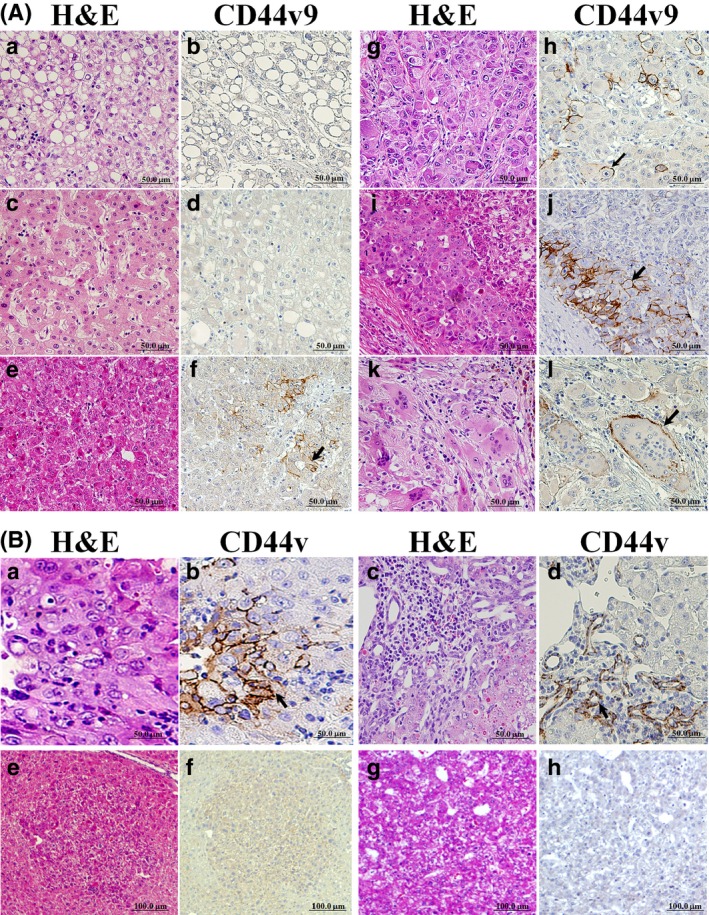
Immunohistochemistry for CD44 variant 9 (CD44v9) in hepatitis C virus‐positive human (A) and mouse (B) hepatocellular carcinomas (HCCs). (A) CD44v9− non‐recurrent HCC (a,b), normal‐appearing liver (c,d), and well (e,f), moderately (g,h), and poorly (i,j and k,l) differentiated CD44v9+ recurrent HCCs. Staining in human HCC used H&E (a,c,e,g,i,k) and CD44v9 (b,d,f,h,j,l). Note CD44v9+ cells (arrows) and positive multinuclear cells (l) in HCCs. (B) In mouse HCCs, note CD44v+ cells (a,b) and positive proliferative ductular epithelial cells in the mixed type tumor (c,d) (arrows). CD44v− basophilic foci (e,f) and hepatocellular adenoma (HCA) (g,h) in mouse liver (serial sections).
