Figure 2.
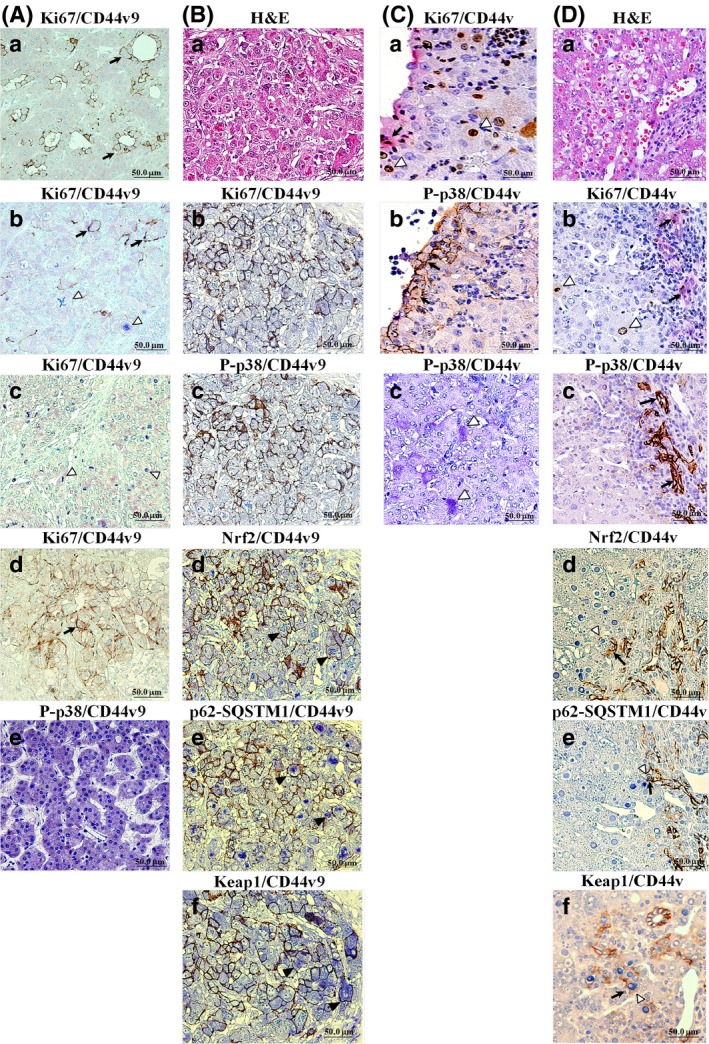
Double immunohistochemistry (IHC) for CD44v (brown/black) and Ki67, phospho‐p38 (P‐p38), nuclear factor (erythroid‐derived 2)‐like 2 (Nrf2), p62‐sequestosome 1 (SQSTM1), or Kelch‐like ECH‐associated protein 1 (Keap1) (blue) in representative cases of recurrent HCV + human and mouse hepatocellular carcinomas (HCCs). (A) IHC for human CD44 variant 9 (CD44v9; black arrows) and Ki67 or P‐p38 (white arrowheads). (a) CD44v9+ and Ki67− moderately differentiated HCC. (b) Independent CD44v9+ and Ki67+ cells in moderately differentiated HCC. (c) CD44v9− and Ki67+ moderately differentiated HCC. (d) CD44v9+ and Ki67− colorectal adenocarcinoma metastatic lesion in the liver (positive control). (e) CD44v9− and P‐p38+ human HCC. (B) H&E staining (a) and double IHC in serial sections for Ki67 (b), P‐p38 (c), Nrf2 (d), p62‐SQSTM1 (e), or Keap1 (f) and CD44v9 in human poorly differentiated HCC. (C) Double IHC for Ki67 (a,b), P‐p38 (c), and CD44v in mouse HCC. (D) H&E staining (a) and double IHC for Ki67 (b), P‐p38 (c), Nrf2 (d), p62‐SQSTM1 (e), Keap1 (f), and CD44v in mouse mixed‐type tumor. Note the inverse correlation between CD44v and Ki67 or P‐p38 and the positive correlations between Nrf2, p62‐SQSTM1, Keap1, and CD44v9 expression (black arrowheads).
