Figure 4.
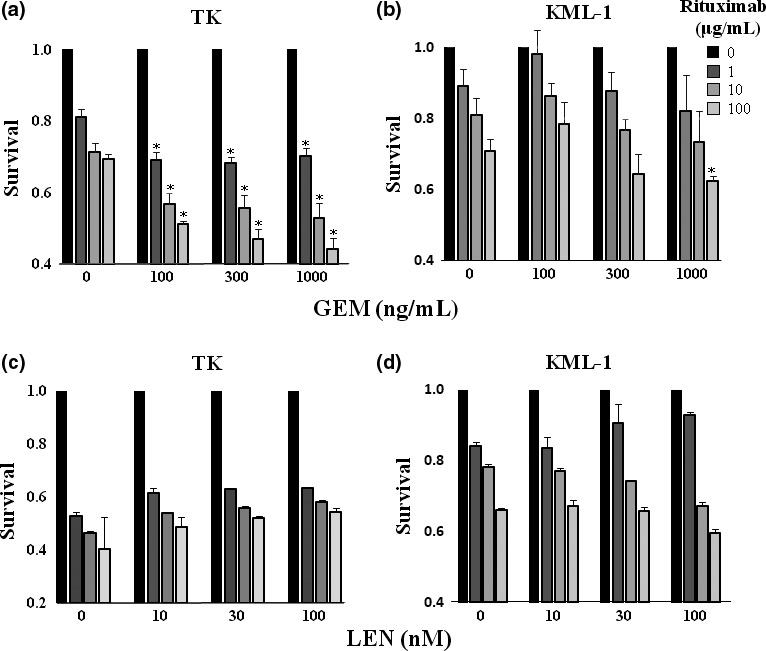
Gemcitabine (GEM) treatment enhanced rituximab‐mediated complement dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) activity. (a) TK cells and (b) KML cells were incubated with GEM (0–1000 ng/mL) and rituximab (0–100 μg/mL) with 10% human AB serum for 48 h. Following staining with propidium iodide (PI), cells were examined for apoptosis by flow cytometry (n = 3). The results were presented as a ratio of the viability of untreated cells to cells treated with GEM. Statistical analysis was performed between the cells treated with both rituximab and GEM and those treated with rituximab alone. P‐values were calculated by Student's t‐test (*P < 0.01). Error bars represent SD. (c) TK cells and (d) KML cells were incubated with LEN (0–100 nM) and rituximab (0–100 μg/mL) with 10% human AB serum for 48 h. Following staining with PI, cells were examined for apoptosis by flow cytometry (n = 3). The results were presented as a ratio of the viability of untreated cells to cells treated with LEN. Statistical analysis was performed between the cells treated with both rituximab and LEN and those treated with rituximab alone. P‐values were calculated by Student's t‐test (*P < 0.01). Error bars represent SD.
