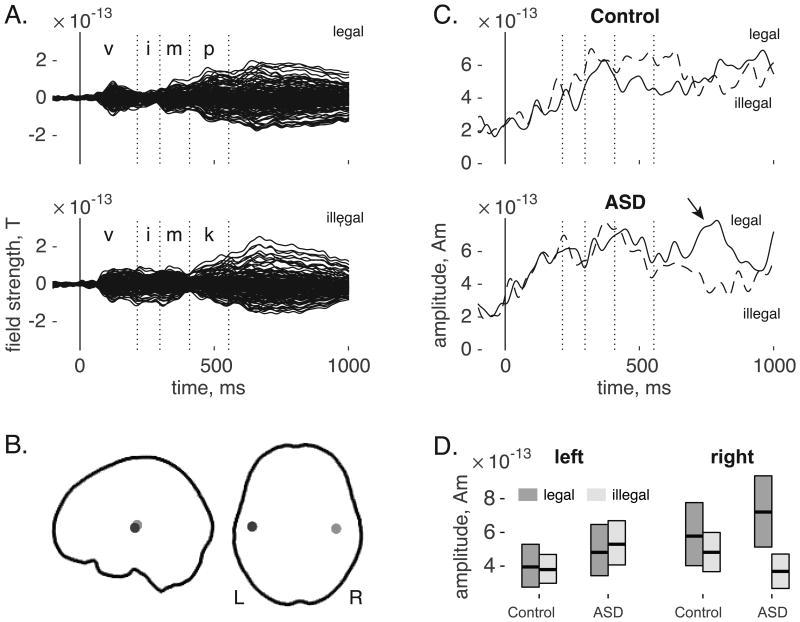
Figure 1.
(A) Grand-averaged sensor waveforms for legal (top) and illegal (bottom) phonotactic sequences. Dotted vertical lines indicate the average latency of phoneme boundaries. (B) Source locations for left (dark grey) and right (light grey) auditory cortex projected on to the cortical envelope of a template brain. (C) Right auditory source waveforms for control participants (top) and children with ASD (bottom). The arrow indicates an effect for phonotactic legality. Dotted vertical lines indicate average latency of phoneme boundaries. (D) Average activity between 750 and 850 ms after stimulus onset, separated by group, source hemisphere, and phonotactic legality. Boxes indicate bootstrap-based 95% confidence intervals.