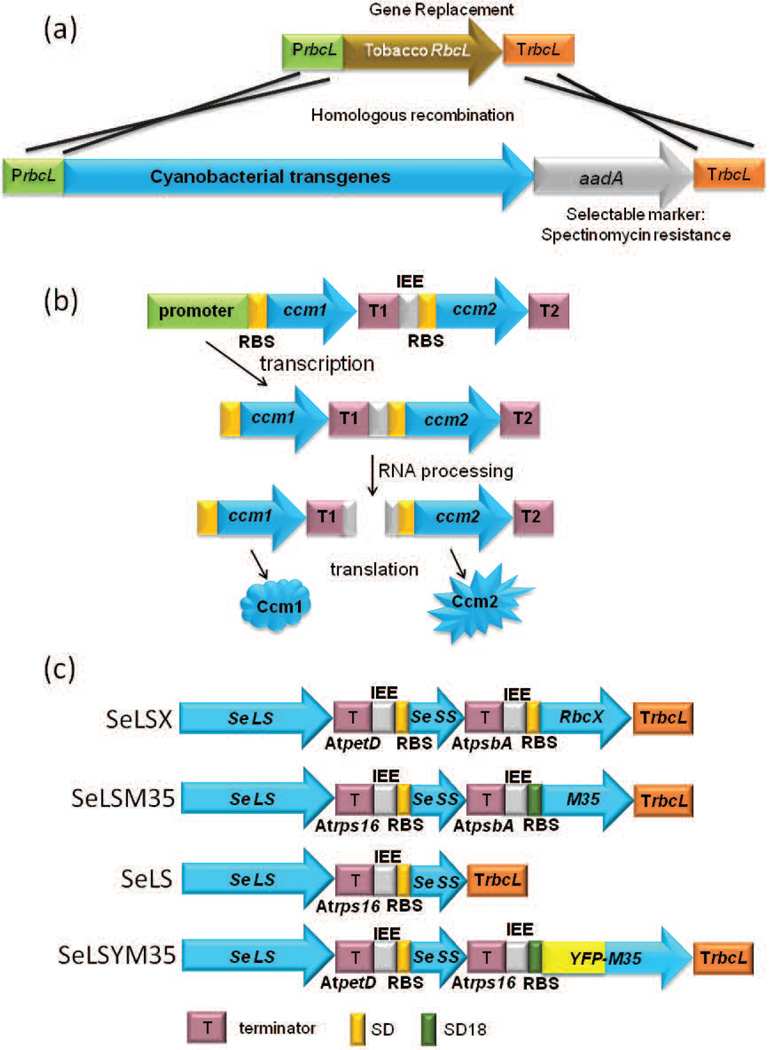
Figure 4.
Schematics of gene arrangements in synthetic operons to express cyanobacterial Rubisco from chloroplasts. (a) Replacement of the tobacco rbcL gene with cyanobacterial transgenes and a selectable marker by homologous recombination. (b) A typical gene arrangement in a synthetic operon with two generic cyanobacterial genes, ccm1 and ccm2. Each gene is followed by a different terminator sequence denoted as T1 or T2. In the intergenic region between ccm1 and ccm2, an intercistronic expression element (IEE) and a ribosome binding site (RBS) are inserted immediately upstream of ccm2 for processing of the dicistronic transcript into monocristronic ones for more efficient translation of the downstream gene, ccm2. (c) Schematics of synthetic operons in four different constructs to express cyanobacterial transgenes from the tobacco rbcL locus (Occhialini, et al. 2016). Se LS, Se SS, RbcX, and M35 represent rbcL, rbcS, rbcX, and ccmM35 genes from S. elongatus PCC7942 respectively. RBS: ribosome binding site. Single (SD) or triple (SD18) Shine-Dalgarno sequences from T7 gene 10 (Drechsel and Bock 2011).