FIGURE 1.
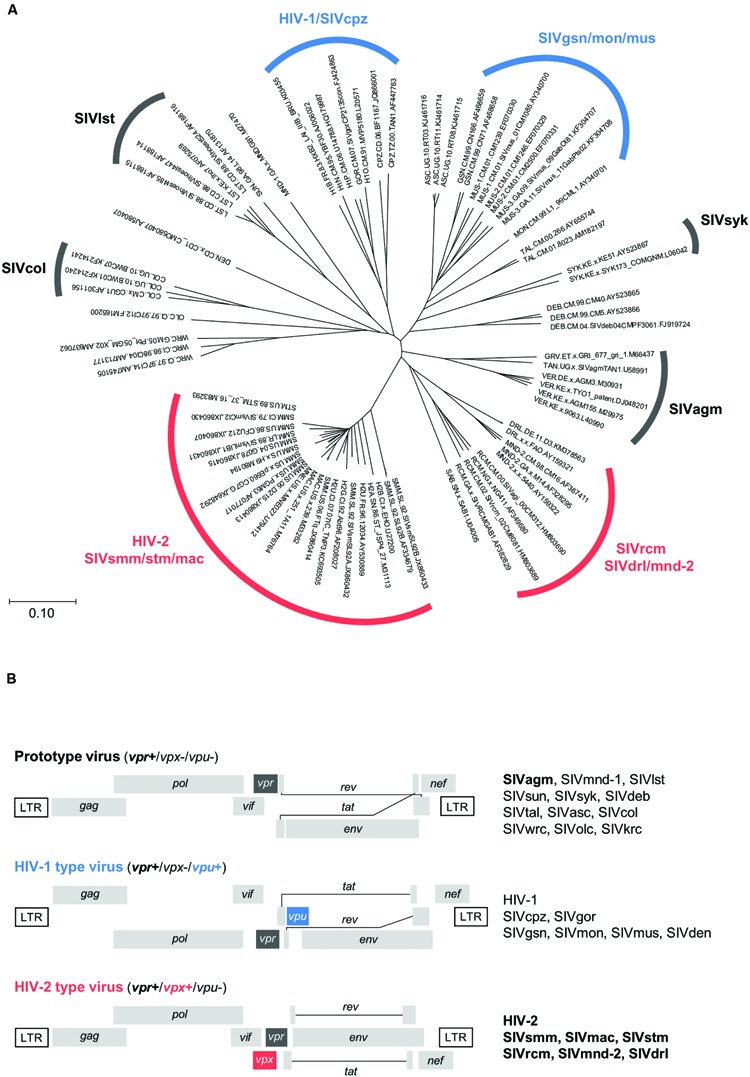
Evolutionary relationship and genome structure of various HIV/SIVs. (A) Phylogeny of HIV/SIVs. The unrooted phylogenetic tree shown was inferred by the neighbor-joining method using amino acid sequences of the entire Gag polyprotein. Amino acid sequences in the HIV Sequence Compendium (http://www.hiv.lanl.gov) were used to generate the tree. Scale bar represents the genetic distance. Eight major viral lineages (Peeters and Courgnaud, 2002; Gordon et al., 2005) are marked as shown. Virus clones not yet classified into the lineage groups remain unmarked. Three genome types (Fujita et al., 2010) are indicated by black (prototype), blue (HIV-1 type), and red (HIV-2 type) letters/lines (see B). (B) Three types of the HIV/SIV genome organization. Genome structures are schematically shown. Letters in boldface type on the right show the lineages analyzed in this study. For virus designations, see Section “Materials and Methods.”
