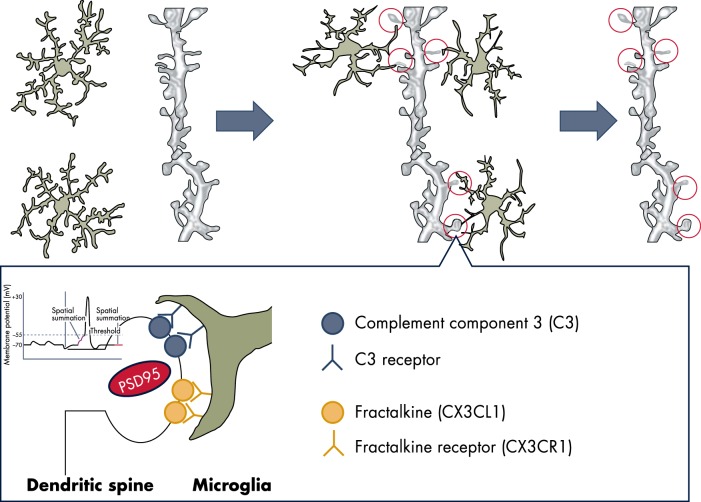
Figure 1.
Microglia are a dynamic mediator of synaptic development and homeostasis. Microglia in its surveying state senses the state of activity of neurons, is attracted to the dendritic spines through proteins of the complement and fractalkine, and participates in neuronal plasticity potentially through the release of proteases able to modulate the structure and functions of the synapses. Microglia possibly respond to the release of ATP, which may induce the shedding of lipid-rich vesicles that were reported to increase the frequency and amplitude of the excitatory postsynaptic potential.