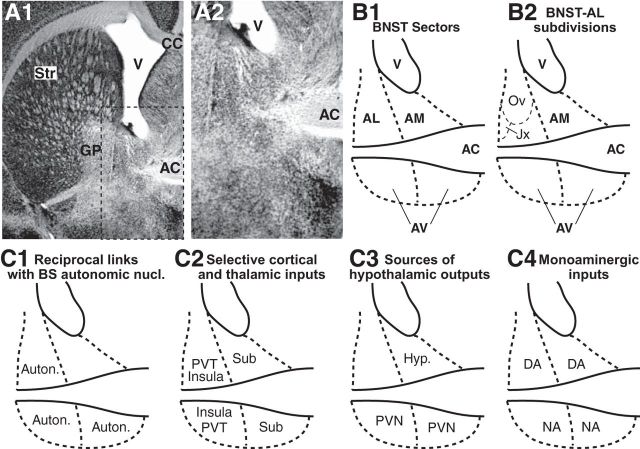
Figure 1.
Structure and main connections of BNST. A, Anterior BNST at low (1) and high (2) magnification. Coronal sections processed to reveal NeuN immunoreactivity. B, Nomenclature. C, Connections. Two major fiber bundles, the intra-BNST segment of the stria terminalis (ST) and the anterior commissure (AC), naturally divide the anterior part of BNST in three sectors: Dorsal to the AC are the AL and AM sectors, located lateral and medial to the ST, respectively. Ventral to the AC is the AV region. In contrast with BNST-AL, BNST-AM receives little or no CeA inputs (see references in main text), (1) it does not project to brainstem autonomic centers (C1) (Norgren, 1976; Ricardo and Koh, 1978; Saper and Loewy, 1980; Schwaber et al., 1982; Sofroniew, 1983; Gray and Magnuson, 1987, 1992; Shin et al., 2008; Panguluri et al., 2009; Bienkowski and Rinaman, 2013); (2) it is innervated by largely distinct cortical areas and thalamic nuclei (C2) (Cullinan et al., 1993; McDonald et al., 1999; Reynolds et al., 2005; Li and Kirouac, 2008; Shin et al., 2008; Bienkowski and Rinaman, 2013); and (3) moreover, its hypothalamic projections are comparably massive (C3) (Conrad and Pfaff, 1976a, b; Saper et al., 1976; Swanson, 1976; Swanson and Cowan, 1979; Kita and Oomura, 1982a; b; Dong and Swanson, 2003, 2004, 2006a, b, c; Dong et al., 2000, 2001b). Although the connectivity of the lateral and medial portions of BNST-AV is similar to that of BNST-AL and AM, respectively, it must be considered separately because of its heavy noradrenergic innervation, among the densest in the brain (C4) (Fallon and Moore, 1978; Forray et al., 2000), as well as its strong projections to the VTA (Dong et al., 2001b; Georges and Aston-Jones, 2002) and PVN of the hypothalamus (Sawchenko and Swanson, 1983; Moga and Saper, 1994). AC, Anterior commissure; Auton, autonomic centers; BS, brainstem; CC, corpus callosum; DA, dopamine; GP, globus pallidus; Hyp, hypothalamus; Jx, juxtacapsular; NA, noradrenaline; Ov, oval; PVT, paraventricular nucleus of thalamus; Sub, subiculum; Str, striatum; V, ventricle.