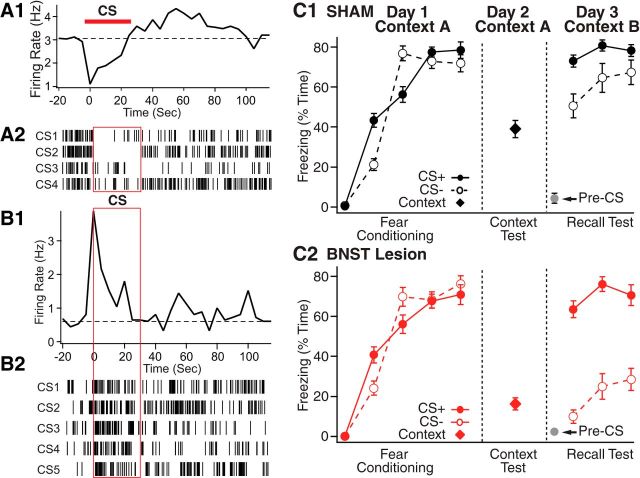
Figure 6.
BNST activity alters the processing of discrete threatening stimuli. A, B, Two examples of anterior BNST neurons with short-latency responses to discrete threatening cues. These cells were recorded extracellularly in rats that had been subjected to a classical auditory fear conditioning protocol (CS, conditioned stimulus, pure tone). We show CS-evoked activity during the recall test, conducted 1 d after conditioning. A1, B1, Peri-CS histograms of neuronal discharges. A2, B2, Rasters where each tick represents an action potential. Cells with inhibitory responses prevailed in BNST-AL, whereas cells with excitatory responses were concentrated in BNST-AM. C, Excitotoxic BNST lesions enhance the stimulus specificity of conditioned fear responses. The two graphs compare percentage time freezing to the CS+ (filled symbols and solid lines), CS− (empty symbols and dashed lines), or conditioning context exposure in sham (C1, black) or BNST-lesioned (C2, red) rats. There is markedly reduced freezing to the CS− with no change in behavior to the CS+ in BNST-lesioned rats. C, Modified from Duvarci et al. (2009).