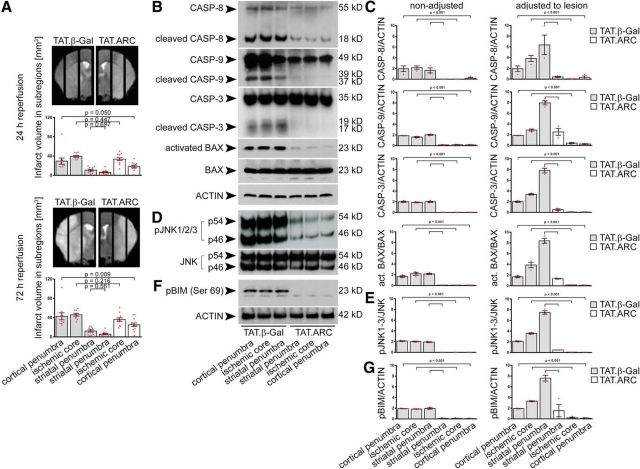
Figure 3.
Administration of TAT.ARC protein attenuates focal ischemic brain injury in the cortical penumbra but attenuates cell death signaling independent of ischemic subregions. A, In analogy to the biochemical analysis, ischemic hemispheres were divided into 2 mm sagittal slices for regional lesion volume analysis after 60 min MCAo and quantified as described in Materials and Methods. Gray bar graphs indicate TAT.β-Gal-treated mice, and open bar graphs indicate TAT.ARC-treated mice. Data are presented as mean and scattered dot plots ± SEM. T2 stroke volumes were analyzed by two separate mixed linear regression models with Sidak's post hoc analysis. B–G, Immunoblots show blocked formation of cleaved caspase-8, caspase-9, caspase-3, and BAX activation (B, C), reduced JNK activity (D, E), and blunted BIM phosphorylation (F, G) in response to TAT.ARC administration compared with TAT.β-Gal-treated mice. Different ischemic zones are shown as indicated. Data are representative of three independent experiments (B, D, F). Mixed linear regression models were applied for semiquantitative densitometric Western blot analysis of three animals per TAT protein group and presented as red scattered dot plots per animal and mean ± SEM. Quantification was referred to the indicated reference protein and the dilution factor of healthy tissue within a subregion (characterized by T2 intensity in MRI) was used to adjust the Western blot signal to the lesion (for details, see Materials and Methods).