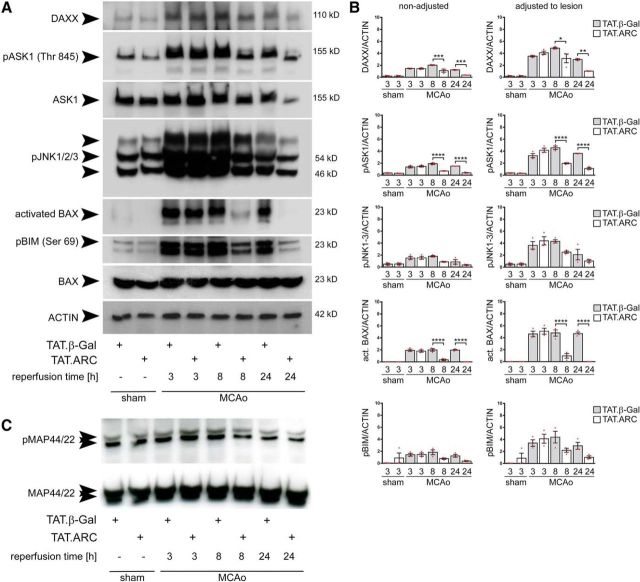
Figure 4.
TAT.ARC-mediated inhibition of DAXX–ASK1–JNK signaling during focal ischemic infarction. A, Immunoblots demonstrate that TAT.ARC attenuates ischemia-induced activation of the DAXX–ASK1–JNK signaling pathway at 24 h after ischemia compared with the corresponding area in TAT.β-Gal-treated mice. The blots are representative of three independent experiments. B, Semiquantitative analysis of immunoblots of three mice are presented as mean and scattered dot plots ± SEM. The right panel was adjusted to lesion volume as measured by T2 sequence in MRI in the core slice after 24 h. DAXX, pASK1, and activated BAX showed significant TAT treatment × time interactions as analyzed by two-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey's post hoc analysis. pJNK1-3 showed significant treatment (p = 0.03) and time (p = 0.0002) effects but no interaction (p = 0.0988). pBim showed no significant treatment × time interaction (p = 0.065). Post hoc tests were significant as indicated by asterisks between TAT β-Gal and TAT.ARC comparisons per time point in the graphs. C, Immunoblots show no effects on MAP44/42 kinase pathway in response to TAT.ARC administration compared with TAT.β-Gal-treated mice. Different reperfusion times from the middle ischemic slice are shown as indicated. Data are representative of three independent experiments.