Figure 6.
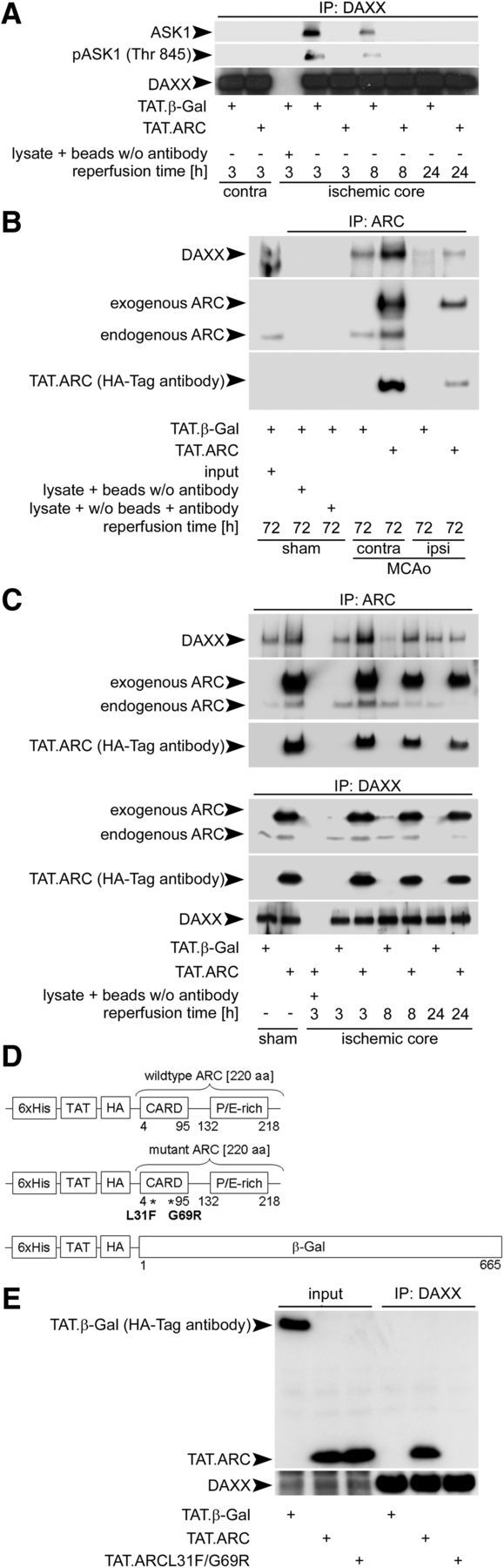
ARC interacts with DAXX and prevents DAXX–ASK1 binding. A, Exogenous ARC prevents DAXX–ASK1 binding. Brain extracts from the middle slice of the reperfusion or corresponding contralateral slice were immunoprecipitated using anti-DAXX antibody. Immunoprecipitates were immunoblotted for DAXX and ASK1, respectively. Brain lysates of the middle slices plus beads without anti-DAXX antibody served as internal loading controls. B, ARC binds DAXX in the cerebral cortex under physiological and ischemic conditions 72 h after reperfusion. Brain homogenates of the middle slices were immunoprecipitated with anti-ARC antibody and immunoblotted with antibodies against DAXX, ARC, and HA. Brain lysate plus beads without anti-ARC or lysate plus anti-ARC antibody without beads served as controls. C, Endogenous and exogenous ARC interacts with endogenous DAXX in vivo. Immunoprecipitation of brain lysates of the middle slice after ischemia or sham operation were performed with anti-ARC or anti-DAXX as primary antibodies. Brain lysates plus beads without anti-ARC or anti-DAXX antibody served as controls. D, Domain structures of TAT proteins with their tags and mutations. His, Histidin tag; HA, hemagglutinin tag; P/E-rich, proline/glutamate rich domain; β-Gal, β-galactosidase; L, leucine; F, phenylalanine; G, glycine; R, arginine. E, ARC interacts via its CARD domain with DAXX. Brains were transduced with TAT.β-Gal, TAT.ARC, or TAT.ARC.mutant (L31F; G69R) and immunoprecipitated with anti-DAXX antibody. Immunoblots were probed as indicated and derived from two mice and replicated in triplicate.
