Figure 8.
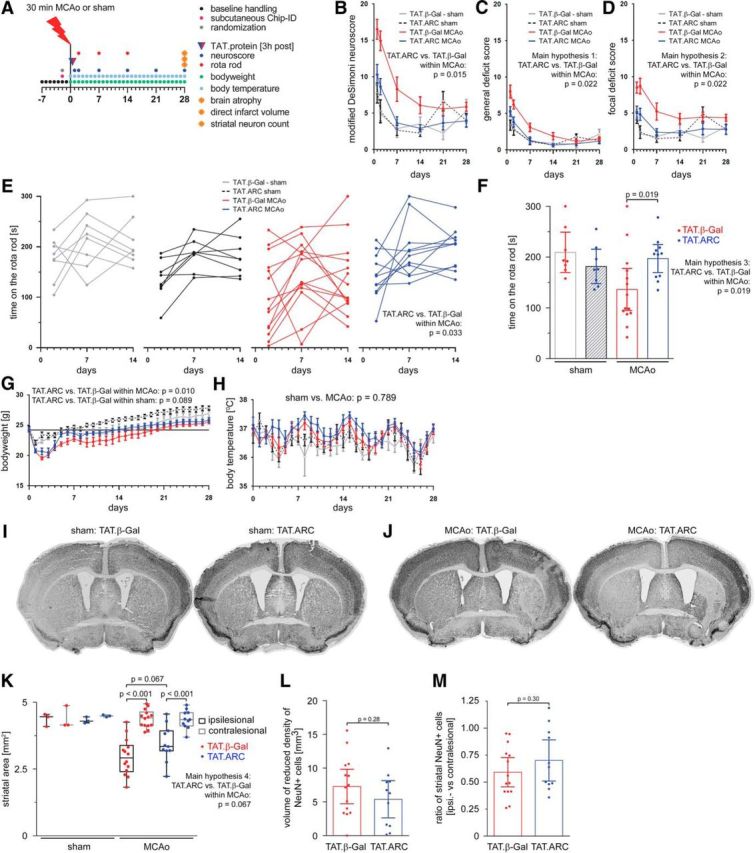
Delayed administration of TAT.ARC protein attenuates focal ischemic brain injury and fosters recovery in the long term. A, Experimental setup of MCAo, 3 h delayed intrathecal application of 5 μg of TAT proteins, and reperfusion time points for distinct analyses. Composite modified DeSimoni neuroscore (B) with general (C) and focal deficit (D) scores and rotarod data (E, F). Rotarod data after 14 d is shown as the mean time on the rod with CIs. G, Body weight was measured before surgery (day 0) and after non-invasive transponder-mediated body temperature measurements (H). Data in B–D and G, H are presented as mean ± SEM and in F, L, and M as mean ± CI. I, Multiple image alignment of neuronal staining using anti-NeuN–DAB of sham mice and 28 d after MCAo (J). Striatal area in coronal section a3 (K) in both ipsilateral and contralateral hemispheres and residual infarct area/scar as defined by decreased neuronal density (L) and ratios of ipsilesional versus contralesional neurons counted in TAT.β-Gal or TAT.ARC mice (M) were illustrated by scatter dot plots and box and whiskers (minimum to maximum) for K and mean + CI (L, M).
