Figure 1.
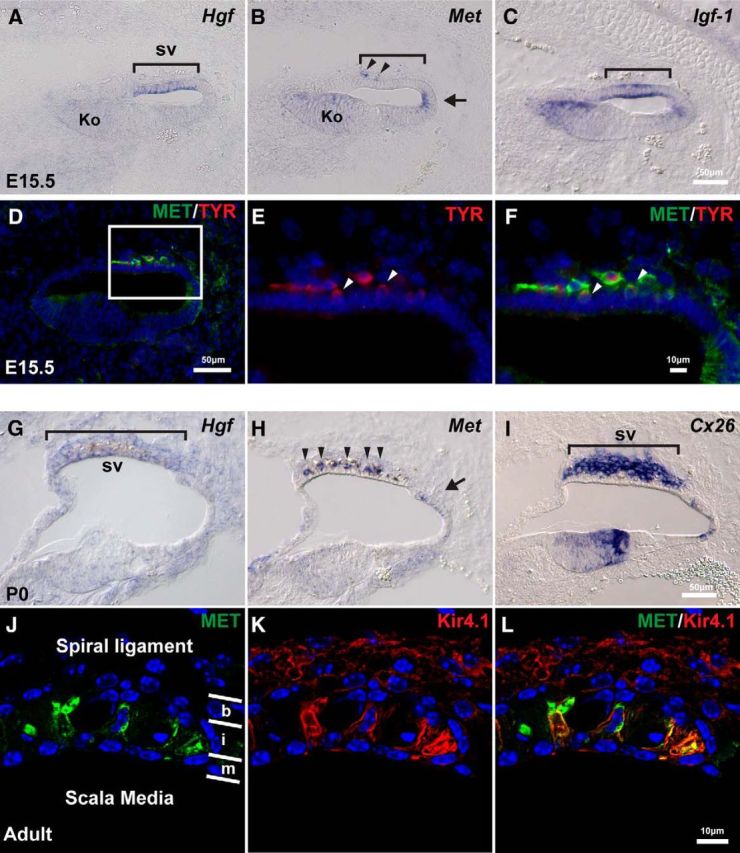
Hgf and c-Met are expressed in the developing mouse cochlea. A, At E15.5, Hgf is expressed in the future stria vascularis (sv; bracket). B, c-Met is expressed weakly in the entire cochlear epithelium. Slightly higher expression is observed in Kölliker's organ (Ko) and the domain adjacent to future stria vascularis (arrow). A few c-Met+ cells are observed in mesenchyme adjacent to the future stria vascularis region (arrowheads). C, Igf-1 is expressed in the future stria vascularis (bracket). D, c-Met+ (green) cells in the mesenchyme (similar cells in B) express a melanocyte marker, tyrosinase (red). E, F, Higher magnification of the region of future stria vascularis indicated with a rectangle in D. Some of the c-Met+; Tyrosinase+ cells appear to becoming incorporated into the epithelium (arrowheads). G, At P0, Hgf is weakly expressed in the stria vascularis (bracket). H, c-Met is expressed in the intermediate layer of the stria vascularis (arrowheads) and the domain adjacent to the stria vascularis (arrow) at P0. I, Connexin 26 (Cx26) is expressed in the basal layer of the stria vascularis. J–L, Higher magnification of the stria vascularis in adult mice. Layers of basal cells (b), intermediate cells (i) and marginal cells (m) are divided by white lines. c-Met protein (green) is colocalized with an intermediate cell marker, Kir4.1 (red).
