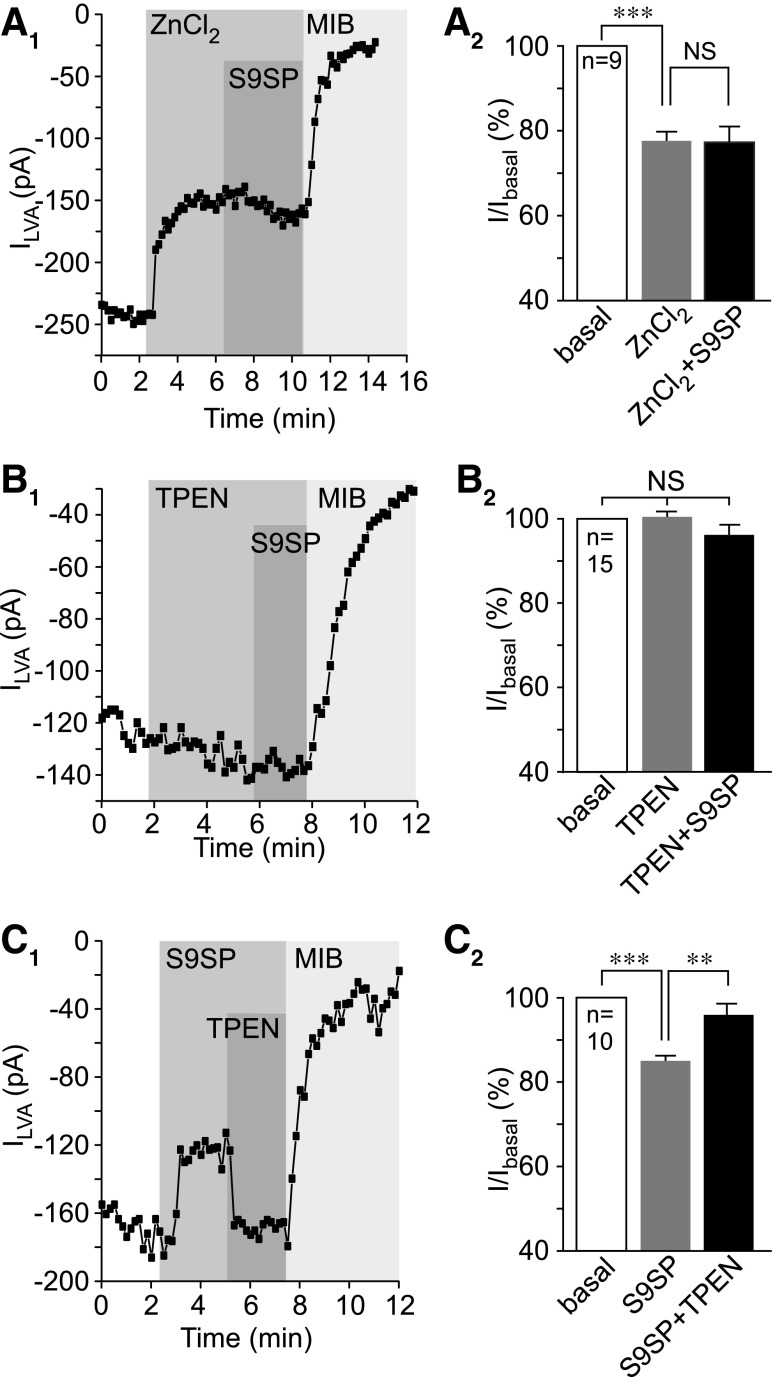
FIG. 4.
Extracellular zinc mimics SP action on T-type Ca2+ channels. (A) Extracellular ZnCl2 inhibited LVA Ca2+ currents in DRG neurons. (A1) Example time course of the effect of ZnCl2 (750 nM), S9SP (1 μM), and MIB (3 μM) on the LVA Ca2+ current recorded form small-diameter DRG neurons using whole-cell patch clamp. Periods of drug application are indicated by the vertical gray bars; (A2) summarizes the effects. (B) Zinc chelator TPEN (10 μM) prevents SP-mediated LVA current inhibition in DRG neurons. (B1) Example time course of the effect of TPEN (10 μM), S9SP (1 μM), and MIB (3 μM) on the LVA current; (B2) summarizes the effects; layout and labeling are similar to (A). (C) TPEN reverses the SP-induced LVA current inhibition in DRG neurons. (C1) Example time course of the effect of S9SP (1 μM), TPEN (10 μM), and MIB (3 μM) on the LVA current; (C2) summarizes the effects; layout and labeling are similar to (A, B). Asterisks indicate significant difference from the group indicated by the line connector with **p < 0.01 or ***p < 0.001 (paired t-test). In all bar charts, data are shown as mean ± SEM. TPEN, N,N,N′,N′-Tetrakis(2-pyridylmethyl)ethylenediamine.