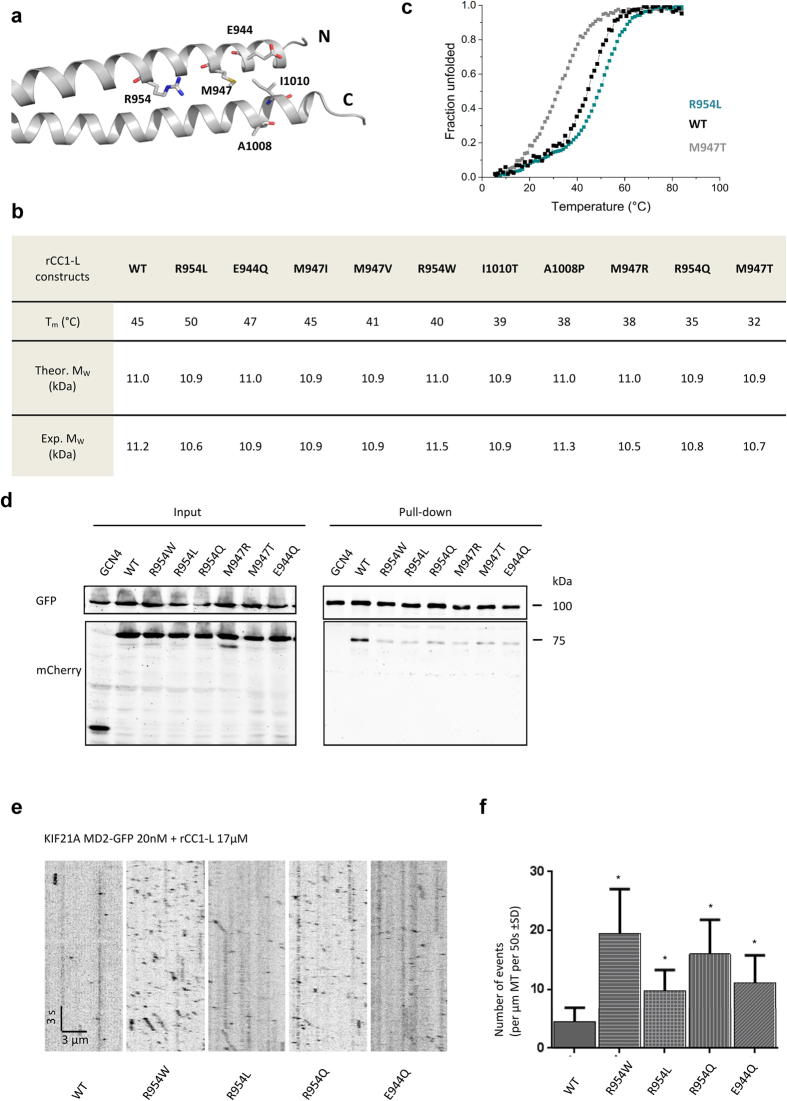
Figure 6. CFEOM1 mutations release KIF21A autoinhibition by destabilizing the regulatory antiparallel coiled coil or by affecting residues of the binding interface.
(a) Positions of the CFEOM1-associated amino-acid residues shown in one half of the KIF21A rCC1 crystal structure. Amino (N) and carboxy (C) termini are indicated. (b) Summary of the biophysical characterization of wild-type rCC1-L and its CFEOM1 mutants by thermal unfolding monitored by CD at 222 nm using a protein concentration of 0.125 mg/ml and SEC-MALS performed at a protein concentration of 2 mg/ml. (c) Normalized thermal unfolding profiles of wild-type rCC1-L and its most destabilizing (M947T) and most stabilizing mutants (R954L). (d) Streptavidin-based pull-down assay with lysates of HEK293T cells expressing Bio-GFP-tagged KIF21A_MD2 used as bait for the pulldown of mCherry-labelled STALK1_WT and mutant polypeptide chain fragments. (e) In vitro kinesin motility assay. The assay was performed as described in Fig. 5d, but in the presence of wild-type or mutant rCC1-L domains. Values significantly different from the wild-type control are indicated by an asterisk (P < 0.0001, Mann-Whitney U test).