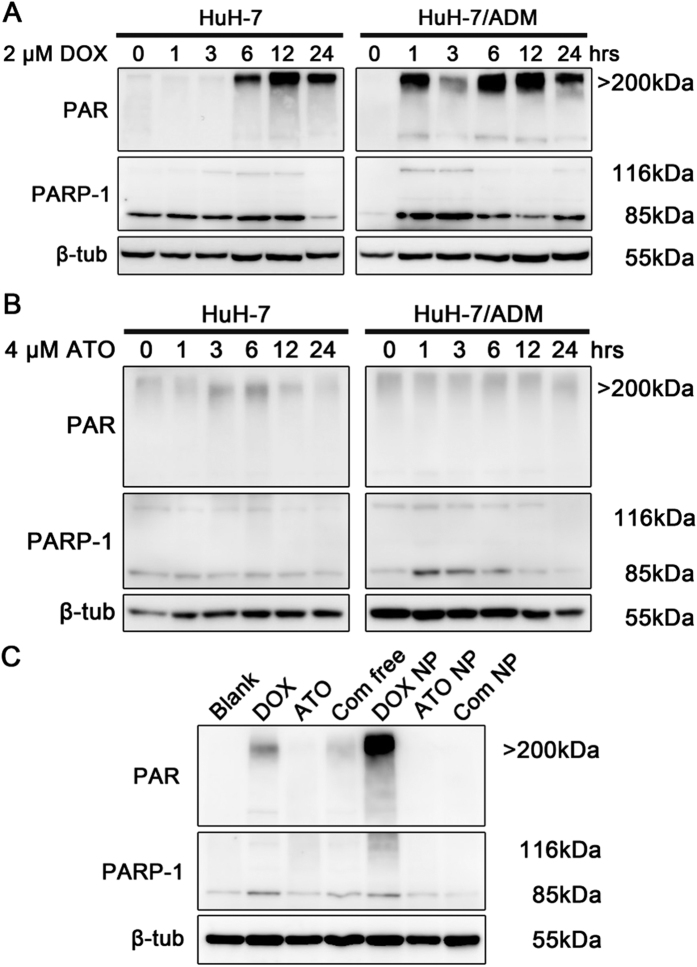
Figure 5. PARP-1 activation after DOX treatment and inactivation after ATO treatment.
The expression levels of PAR, PARP-1 and β-tubulin were detected by western blot. All samples were processed under the same experimental conditions. Cropped gels were used to improve the clarity. (A) HuH-7 and HuH-7/ADM cells were treated with 2 μM DOX for different incubation times. In response to DNA damage caused by DOX, massive PAR was rapidly generated by PARP-1 in HuH-7/ADM cells. (B) HuH-7 and HuH-7/ADM cells treated with 4 μM ATO for different incubation times. HuH-7/ADM cells treated with ATO could not induce the synthesis of PAR. (C) HuH-7/ADM cells were treated with different drug formulations (2 μM DOX and 4 μM ATO) for 12 h. DOX and DOX NP induced activation of PARP-1 and catalyzed PAR polymer production. Nevertheless, expression of PAR was dramatically inhibited in the presence of ATO after combinational treatments, especially Combo NP. Full-length blots with multiple exposures are presented in Supplementary Fig. S7.