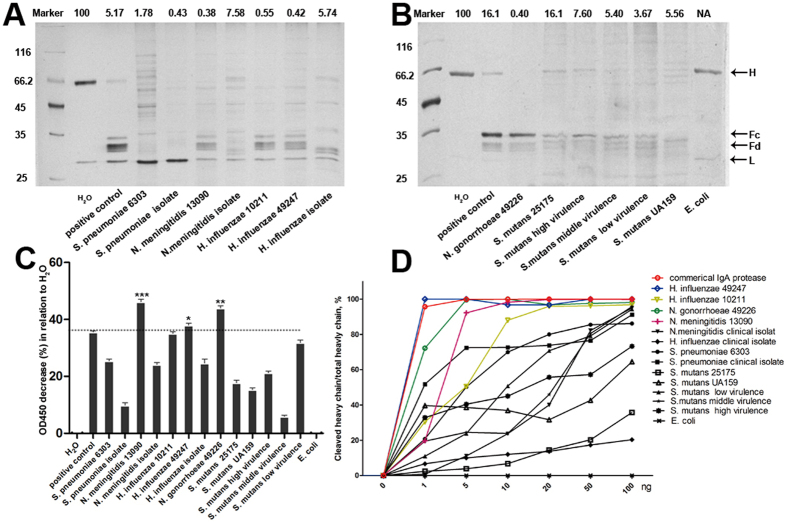
Figure 1. Catalytic activities of IgA proteases from different bacteria.
(A,B) 0.5 μg of human IgA1 was subjected to overnight digestion by 0.05 μg of IgA proteases from indicated bacterial strains. The digestion pattern was resolved by SDS-PAGE electrophoresis. The percentage of the residual heavy chain was indicated up the lane. A commercial IgA protease derived from N. gonorrhoeae was used as positive control. H stands for the heavy chain of IgA1 and L the light chain. Fc and Fd are the final products of digested IgA1 heavy chain. (C) Quantification of catalytic activities of different bacterial IgA protease by ELISA-based assay. Data represent 4 independent replicates and each bar represents mean ± SEM for the percentage of reduction of OD value compared with the negative control (H2O). *P < 0.05 vs positive control. **P < 0.01 vs positive control. ***P < 0.001 vs positive control. (D) Dosage-dependent digestion of IgA1 by IgA proteases. 0.5 μg of IgA1 was incubated with different amount of IgA protease at 37 °C for 2 hours. The digestion mixture was subjected to SDS-PAGE analysis. The percentage of cleaved heavy chain (in relative to the negative control) was ploted. Note the ploted lines for commercial IgA protease, and proteases from N. gonorrhoeae 49226, N. meningitidis 13090, H. influenzae 49247 and 10211 were highlighted colorfully.