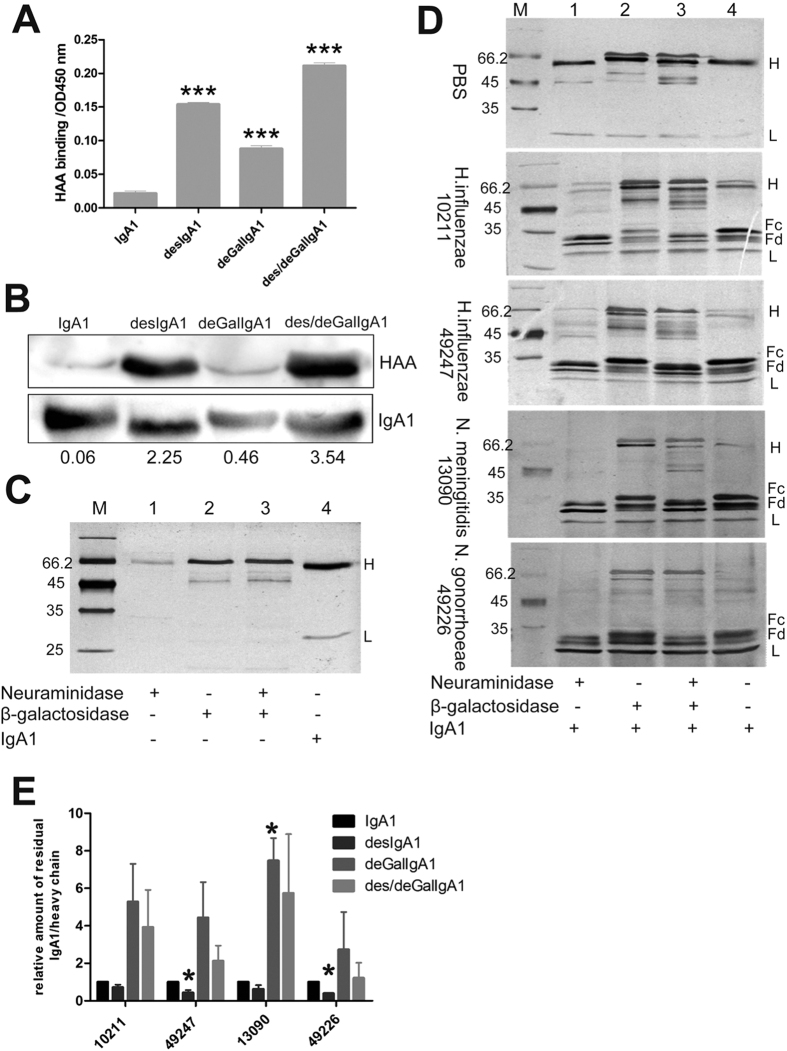
Figure 2. In vitro degradation ability of IgA proteases on deglycosylated IgA1.
(A) Determination of glycosylation level of IgA1 after treatment with different deglycosylation enzyme (β-galactosidase and neuraminidase) by HHA-based ELISA. Each sample was assayed in triplicate and data was presented as mean ± SEM. ***P < 0.001 versus IgA1 group. (B) Western blots for determination of glycosylation level of modified IgA1 using biotin-labeled HAA to recognize GalNAc-exposed IgA1 (upper panel) and IgA1 specific antibody to detect total IgA1 (lower panel). Number below the lanes indicated the relative abundance of Galactose-deficient IgA1. The full-length blots were presented in Supplementary information (Figure S5). (C) SDS-PAGE analysis of neuraminidase, β-galactosidase and IgA1 without treatment with the IgA protease. (D) SDS-PAGE analysis of IgA1 pre-treated with different deglycosylation enzymes and digested with IgA proteases from H. influenzae 10211 and 49247, N. meningitidis 13090 and N. gonorrhoeae 49226. PBS was used as a control. DesIgA1, desialylated IgA1. DeGalIgA1, degalactosylated IgA1. (E)Quantitative analysis of the residual IgA1 (heavy chain) in Panel D. Data represent for 3 independent experiments. *P < 0.05 vs IgA1 group.