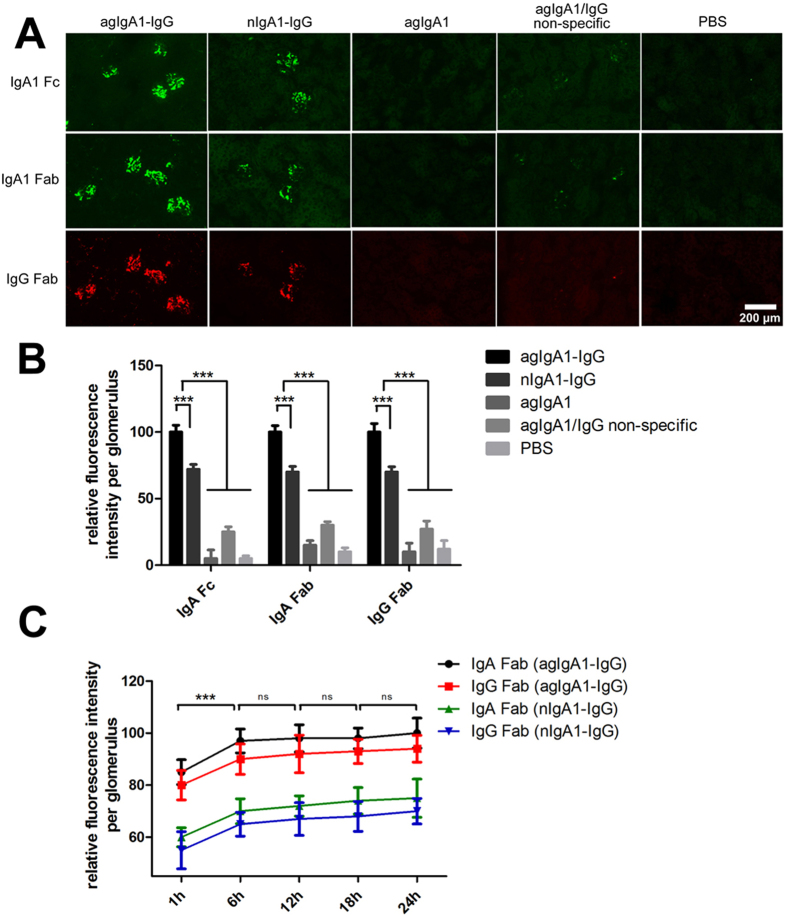
Figure 5. Characterization of the passive IgAN mouse model.
(A) Deposition of IgA-associated immune complexes within mouse glomeruli after 6 hours post-injection of immune complexs (agIgA1-IgG, nIgA1-IgG) or agIgA1 or mixture of free agIgA1 and non-specfic IgG (agIgA1/IgG non-specific). The deposited IgA1 and IgG in glomeruli were detected by anti-human IgA1 (Fc and Fab fragment) or anti-goat IgG (Fab fragment) immunofluorescence. Image represents for sections from 10 mice in each group. (B) Quantitative analysis of the relative immunofluorescence in panel A. Relative fluorescence intensity was normalized to agIgA1-IgG group with assigned value of 100. (C) Quantitative analysis of immunofluorescent intensity of IgA1 and IgG components in passive IgAN mouse model at indicated time point post-injection of immune complexs. The relative fluorescence intensity was normalized to the glomerulus showing greatest fluorescence with assigned intensity value of 100. Data represents 60 glomeruli on 20 sections from 10 mice for each group in (B,C). ***P < 0.001. ns, no significance. agIgA1, aberrantly glycosylated IgA1; nIgA1, normal IgA1.