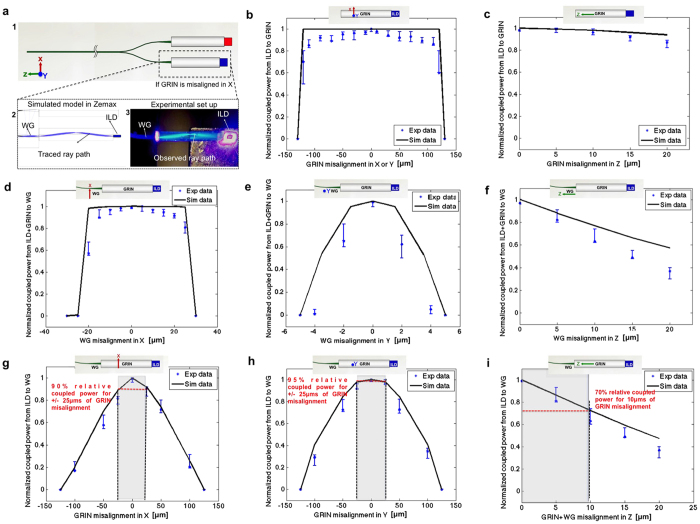
Figure 7. Optical system alignment tolerance analysis to evaluate assembly reproducibility and yield.
(a) Optical model components: (1) Schematic of model components showing ILDs and GRINs coupled to the waveguide mixer (WG); (2–3) Agreement between simulated models in Zemax and experimental results obtained when GRIN lens is intentionally misaligned by 25 μm (in X-axis) while ILD and GRIN are kept stationary. The traced ray path in Zemax (2) matches very well the observed ray path in the assembled prototype device (3). (b,c) Alignment tolerance analysis for ILD-GRIN coupling when ILD is stationary but GRIN is (b) laterally misaligned in X or Y-axis (because GRIN lens is symmetrical about X and Y axis, misalignment in either directions leads to the same results); and (c) longitudinally misaligned in Z-axis. (d–f) Alignment tolerance analysis for ILD-GRIN-WG coupling when ILD and GRIN are perfectly aligned and stationary but WG is (d) laterally misaligned in X-axis; (e) laterally misaligned in Y-axis; and (f) longitudinally misaligned in Z-axis. (g–i) Alignment tolerance analysis for ILD-GRIN-WG coupling when ILD and WG are perfectly aligned and stationary but GRIN is (g) laterally misaligned in X-axis; (h) laterally misaligned in Y-axis; and (i) longitudinally misaligned in Z-axis (when GRIN displaces in Z-axis, WG displaces in Z-axis too). The inset for all graphs shows the schematic of the respective coupling interface, depicting the axis and direction of misalignment. Data points show the median of the collected data (N = 3), and error bars represent the range.