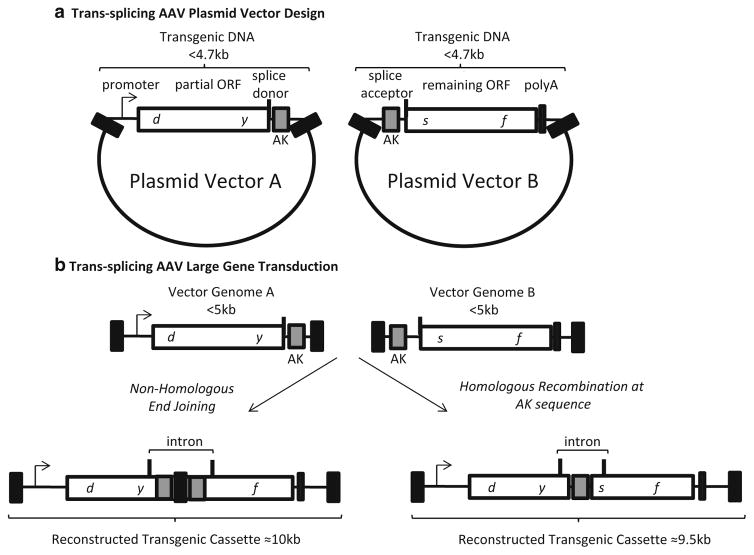
Fig. 2.
Trans-splicingAAV vector design and transduction. (a) The genetic elements of the two required AAV plasmids are depicted. Plasmid A contains a promoter, a partial open reading frame terminated at a splice donor site, followed by a recombinogenic sequence (hybrid vectors only, AK). The vector B plasmid contains a recombinogenic sequence (hybrid vectors only, AK), a splice acceptor site, the remaining ORF followed by a poly A sequence. The transgenic DNA in each plasmid is less than 4 kb. (b) Following co-transduction vector genomes A and B can undergo end joining (left) or homologous recombination at the AK sequence (right) to reconstruct a large transgenic cassette containing the depicted intron. Black box AAV inverted terminal repeat