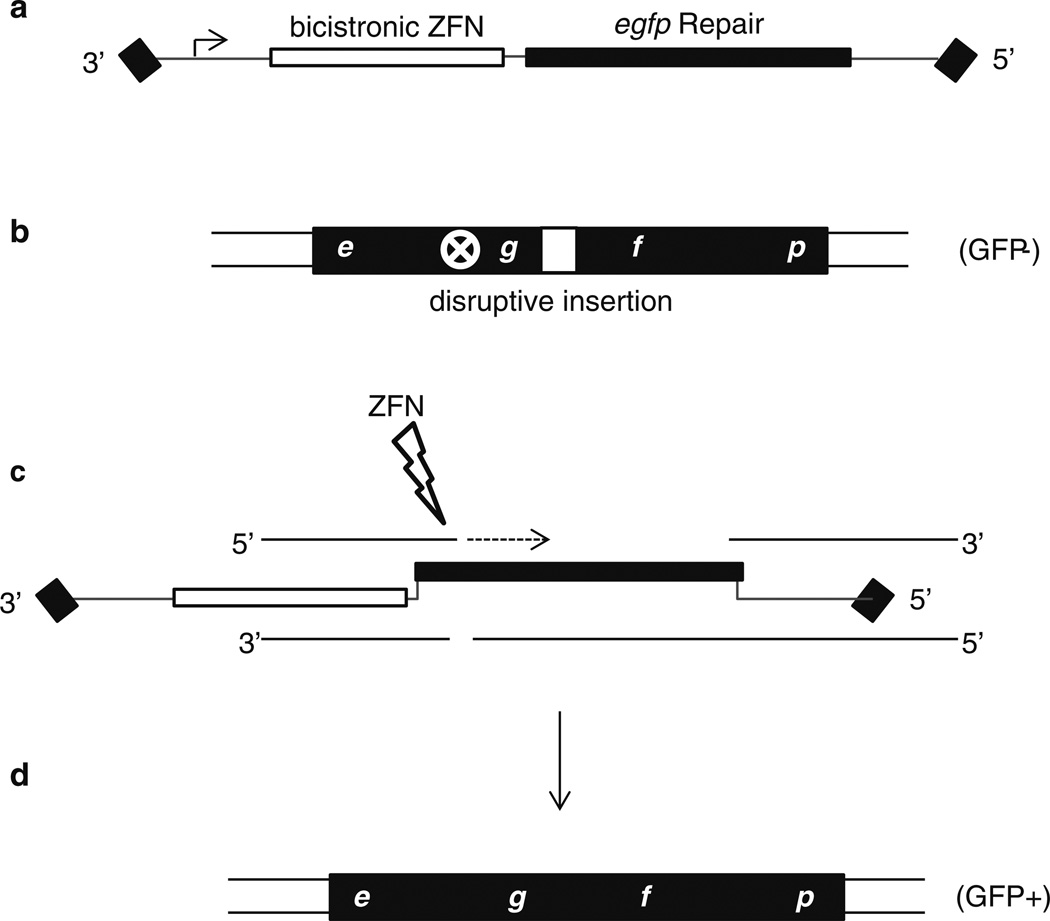
Fig. 3.
AAV vector mediated gene editing. In the depicted cartoon, the transduced AAV genome (a) encodes a promoter, an eGFP-specific ZFN (target site is indicated by a white circled X), and an eGFP repair sequence to correct the defective chromosomal fluorescent reporter (b). In this system, the endonuclease generates a specific double-strand break inducing a host DNA damage response (c). Multiple repair mechanisms can result in correction of the defective reporter using the repair sequence provided by the AAV vector. In this cartoon, we demonstrate an example based on gene conversion in which the AAV repair homology serves as a synthesis template for the free 3′ end generated by the ZFN (c). This new synthesis integrates the desired genetic modification (in this case egfp coding sequence devoid of the insertion represented by the white box) creating, in this example, a functional fluorescent reporter (d)