Fig. 2.
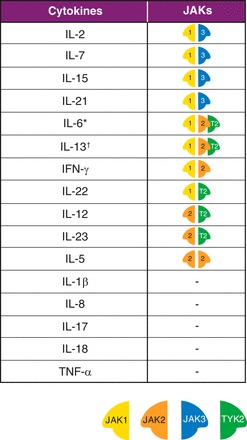
Key cytokines in IBD and Janus kinase (JAK) combinations for cytokines that depend on JAK pathways for signaling. The pairing of JAKs is significant to their role in cytokine signaling, with each member of the JAK family exhibiting preferential binding to the intracellular domains of individual cytokine receptor chains. JAK1 pairs with JAK3 to control signaling of the γ-common cytokines, including IL-2, IL-7, IL-15, and IL-21. Type II cytokine receptors, such as those for the gp130 subunit-sharing receptors, include IL-6 signal mainly through JAK1, but are also associated with JAK2 and tyrosine kinase (TYK) 2. IL-13 signals are through receptors associated with JAK1 and either JAK2 or TYK2. JAK2 is unique in pairing with itself and controls signaling for IL-5. Other key cytokines in IBD that signal using JAKs include IFN-γ (JAK1/JAK2), IL-22 (JAK1/TYK2), and IL-12 and IL-23 (JAK2/TYK2). IL-1β, IL-8, IL-17, IL-18, and TNF-α are other important cytokines in IBD, but do not signal directly using JAKs. An important indirect effect of JAK2/TYK2 blockade for IBD is the downstream inhibition of IL-17 production achieved through direct inhibition of IL-23 signaling. *Type II cytokine receptors, such as those for the gp130 subunit-sharing receptors, including IL-6, signal mainly through JAK1, but are also associated with JAK2 and TYK2. †IL-13 signals are through receptors associated with JAK1 and either JAK2 or TYK2.
