Fig. 7.
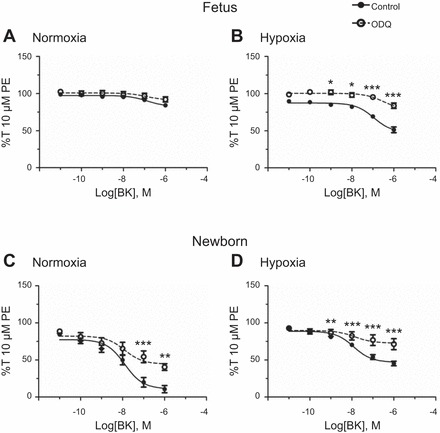
Soluble guanylate cyclase inhibition suppresses bradykinin-mediated relaxation. A–D: dose-response curves of pulmonary arterial rings exposed to 10 pM-1 μM bradykinin in an additive manner normalized to %T10 μM PE for fetal sheep exposed to normoxia and prenatal chronic hypoxia and newborn sheep exposed to normoxia and prenatal chronic hypoxia in the presence of DMSO (control) and 10 μM 1H-[1,2,4]oxadiazolo[4,3-a]quinoxalin-1-one (ODQ) to inhibit soluble guanylate cyclase. Lines show resultant fits to the dose-response relationships with a Hill equation. Values are means ± SE. Data were analyzed by 2-way analysis of variance with a Bonferroni posttest analysis for each dose: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs. control.
