Fig. 2.
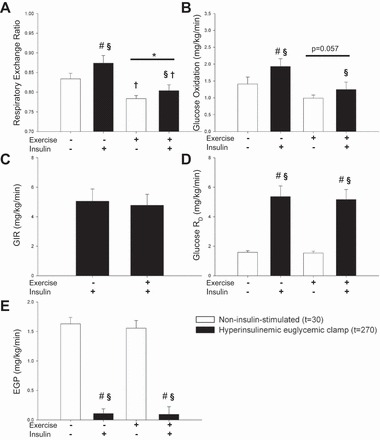
Respiratory exchange ratio, glucose uptake, and glucose metabolism were determined after an overnight fast (rest) and after one h ergometer cycling at 65% VO2-peak (Exercise). Throughout the figure open bars indicate a noninsulin-stimulated condition at t = 30 and closed bars indicate a hyperinsulinemic euglycemic clamp condition at t = 270. A: main effect of experimental day and hyperinsulinemic euglycemic clamp was observed on respiratory exchange ratio (RER). Post hoc testing revealed that exercise decreased RER both during insulin and noninsulin-stimulated conditions, whereas RER increased only during the hyperinsulinemic euglycemic clamp on the resting day. (main effect of experimental day = *P < 0.05, main effect of hyperinsulinemic euglycemic clamp = §P < 0.05, #P < 0.05 vs. basal within experimental day, †P < 0.05 vs. resting within noninsulin-stimulated condition or hyperinsulinemic euglycemic clamp). B and C: glucose infusion rate (GIR) and glucose rate of disappearance (RD) were not affected by exercise, and during the hyperinsulinemic euglycemic clamp, glucose RD was markedly increased. D: there was a trend toward decreased glucose oxidation after exercise. There was a main effect of the hyperinsulinemic euglycemic clamp on glucose oxidation; however, this effect was not significant after exercise when post hoc test was applied. E: endogenous glucose production (EGP) was not affected by exercise and equally suppressed during the hyperinsulinemic euglycemic clamp.
