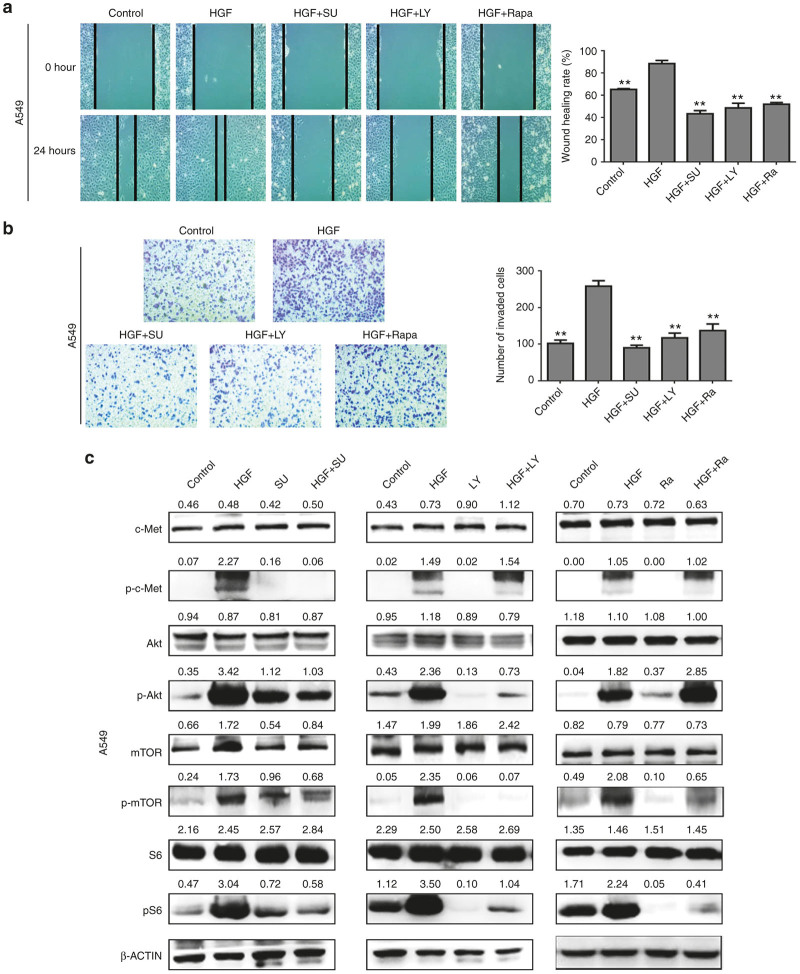
Figure 3.
SU11274, LY294002, rapamycin inhibited hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)-induced lung cancer cell migration, invasion and c-Met/PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling activation. (a,b) A549 cells were starved for 12 hours, then treated with 40 ng/ml of HGF (with 2% fetal bovine serum). MET inhibitors SU11274 (5 μmol/l), or PI3K inhibitor LY294002 (25 μmol/l), or mTOR inhibitor rapamycin (200 nmol/l) was used 1 hour before HGF stimulation. Cell migration capability was determined by wound healing assay (a). Invasion capability was determined by transwell assay (b). Data are means of three separated experiments ± SD, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 compared with HGF group. (c) A549 cells and PC-9 cells were starved for 12 hours, then treated with 40 ng/ml of HGF for 15 minutes. MET inhibitors SU11274 (5 μmol/l), or PI3K inhibitor LY294002 (25 μmol/l), or mTOR inhibitor rapamycin (200 nmol/l) was used 4 hours before HGF stimulation. Protein expression of c-Met, p-c-Met, Akt, p-Akt, mTOR, p- mTOR, S6, and p-S6 were detected by western blotting analysis. Quantitative results are also illustrated. The data presents the average of three independent experiments. SU, SU11274; LY: LY294002; Ra, Rapamycin.