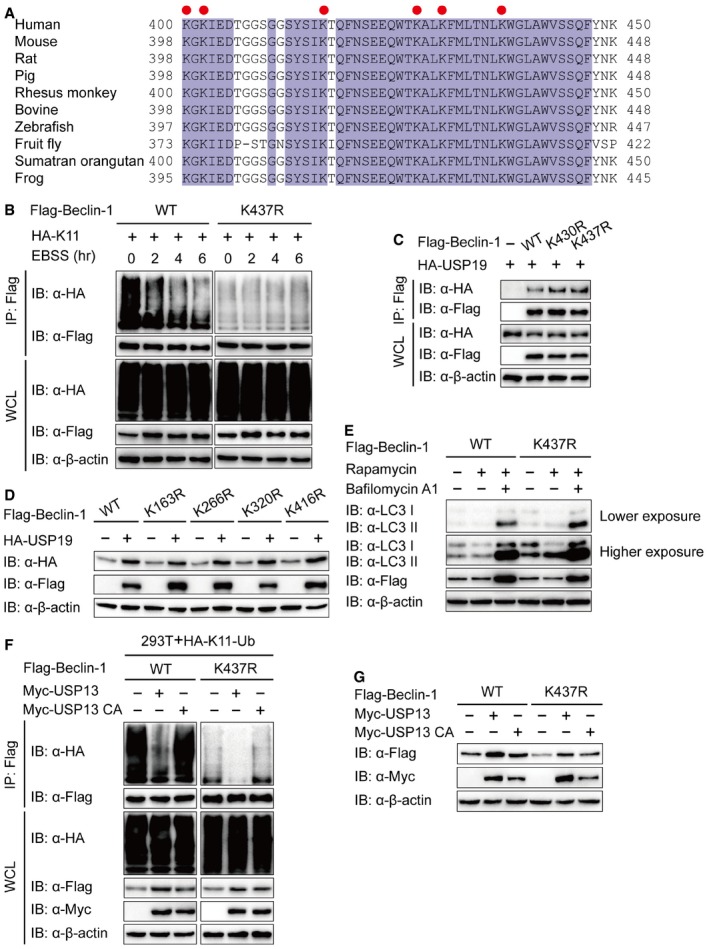
Alignment of Beclin‐1 sequences of different species. Conserved lysine residues are indicated with a red circle.
Lysates of 293T cells transfected with plasmids for Flag‐Beclin‐1 (WT or K437R) and HA‐K11‐Ub were incubated with EBSS medium for the indicated time points, then immunoprecipitation with anti‐Flag beads and immunoblot analysis with anti‐HA.
293T cells were transfected with plasmids encoding HA‐USP19 and Flag‐Beclin‐1 (WT, K430R, or K437R), followed by immunoprecipitation with anti‐Flag beads and immunoblot analysis with anti‐HA.
Immunoblot analysis of extracts of 293T cells transfected with empty vector or vector for HA‐USP19, together with plasmids for Flag‐Beclin‐1 (WT, K163R, K266R, K320R, or K416R).
BECN1 KO 293T cells were transfected with WT or K437R Flag‐Beclin‐1, and lysates were analyzed by immunoblot.
293T cells were transfected with plasmid for Flag‐Beclin‐1 and HA‐K11‐Ub, together with the constructs of USP13 or USP13 enzyme inactivity mutant (C345A (CA)), and the lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti‐Flag and immunoblotted with anti‐HA.
293T cells were transfected with empty vector or vector for Myc‐USP13 (WT or CA), together with plasmid for Flag‐Beclin‐1 (WT or K437R), and the lysates were analyzed with each antibody.