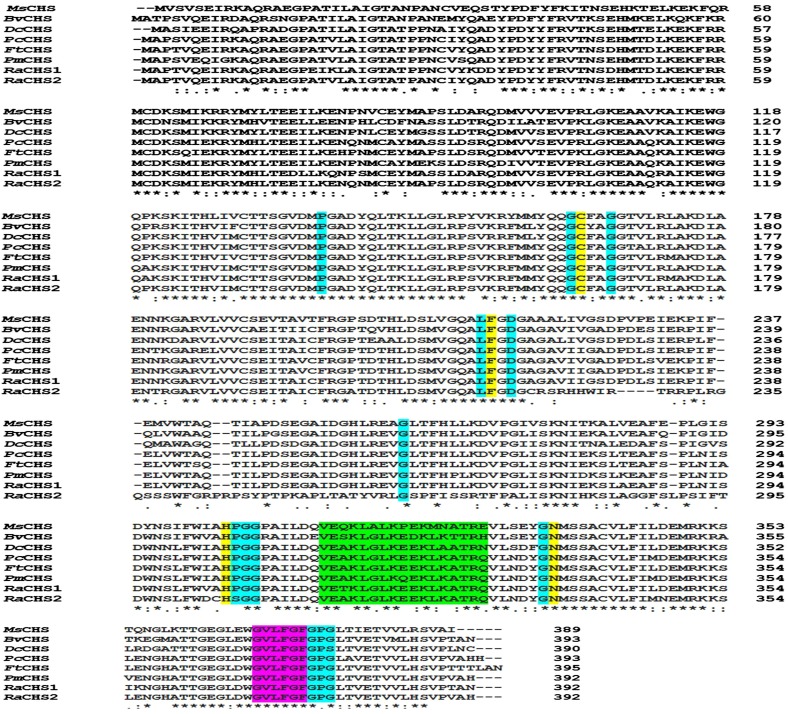
Figure 2.
Multiple sequence alignment of the deduced amino acid sequences of ReCHS1 and ReCHS2 with related plant CHS sequences using the Clustal Omega multiple sequence alignment tool. Amino acid positions are given on the right, and identical, conserved, and semiconserved amino acids are indicated with asterisks, colons, and periods, respectively. Functionally important conserved residues are highlighted with a colored background: yellow, the four catalytic residues (Cys-His-Asp triad + Phe) that are shown to be conserved in all polyketide synthases; cyan, the 13 residues that shape the geometry of the active site; green, the malonyl-CoA-binding motif; and purple, the highly conserved CHS signature sequence, N-myristoylation motif. Abbreviations (with GenBank accession numbers) are as follows: MsCHS, Medicago sativa CHS (L02902); BvCHS, Beta vulgaris CHS (XM_010693892.1); DcCHS, Dianthus caryophyllus CHS (Z67982.1); PcCHS, Polygonum cuspidatum CHS (EF090266.2); FtCHS, Fagopyrum tataricum CHS (HQ434624.1); PmCHS, Persicaria minor CHS (JQ801338.1); RaCHS1, Rheum australe CHS1 (KF850684); and RaCHS2, Rheum australe CHS2 (KC822472).