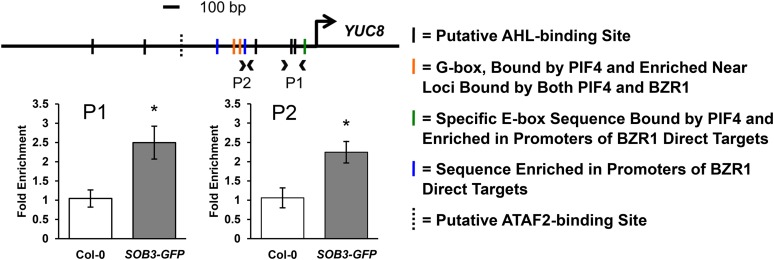
Figure 6.
SOB3 binds to the YUC8 promoter. Relative enrichment is shown within the YUC8 promoter in samples prepared from Col-0 or transgenic SOB3-GFP lines using a ChIP-qPCR procedure employing an antibody against the GFP epitope. Arrowheads on the promoter diagram indicate primer pairs used for qPCR, and the large arrow indicates the transcription start site. Solid black vertical lines on the diagram indicate the presence of one of the five consensus sequences bound by AHLs in the same clade as SOB3 (AATTAAAT and ATTATAAT bound by AHL20; AATATATT bound by both AHL20 and AHL25; and AATTAATT and AATAAAT bound by AHL25; Verkest et al., 2014). Orange lines indicate a G-box motif (CACGTG), which is bound by PIF4 (Huq and Quail, 2002; Hornitschek et al., 2012; Sun et al., 2012) and also enriched in regions of the genome commonly bound by BZR1 and PIF4 (Oh et al., 2012). The green line indicates the presence of a specific E-box motif (CACATG), which is bound by PIF4 (Hornitschek et al., 2012). This motif also is enriched in promoters of genes that are both activated in response to brassinosteroids and directly bound by BZR1 (Sun et al., 2010), as well as in regions of the genome commonly bound by BZR1 and PIF4 (Oh et al., 2012). Blue lines indicate a 5-bp motif (GGTCC) enriched in the promoters of brassinosteroid-regulated genes also bound by BZR1 (Sun et al., 2010). The dashed vertical line indicates the presence of an evening element (AAAATATCT), a potential ATAF2 binding site (Peng et al., 2015). The same set of ChIP samples was used as for Figure 5. All values are shown as fold change compared with the Col-0 control sample. Error bars represent se from three different ChIP preparations. In a Welch’s t test (unpaired two-tailed t test with unequal variance), *, P < 0.05.