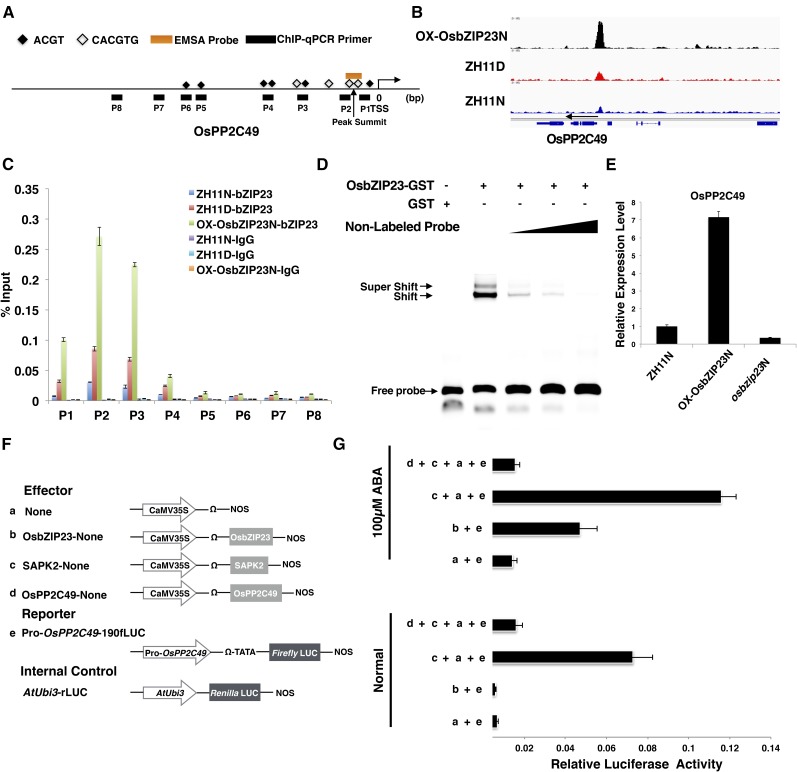
Figure 6.
OsbZIP23 directly and positively regulates the expression of OsPP2C49. A, Scheme showing the structure of the OsPP2C49 promoter region. Short lines indicate the region detected by ChIP-qPCR in C. The black squares indicate the ABREs. The empty squares indicate the G-box (CACGTG). The orange line indicates the location of the probe used for EMSA in D. B, ChIP-Seq data showing OsbZIP23 specifically binding to the promoter region of OsPP2C49. C, Validation of the direct binding of OsbZIP23 to the promoter of OsPP2C49 by ChIP-qPCR. The enrichment values were normalized to Input. D, qRT-PCR showing that OsbZIP23 positively affects the expression levels of OsPP2C49 in rice. Actin was used as a reference gene. E, EMSA showing that OsbZIP23 could directly bind to the promoter of OsPP2C49. The 5-, 10-, and 30-fold excess nonlabeled probes were used for competition. F, Scheme of the constructs used in the rice protoplast cotransfection assay. G, OsbZIP23 activates OsPP2C49 expression in a phosphorylation-dependent manner. The fLUC/rLUC ratio represents the relative activity of the OsPP2C49 promoter. After transfection, half of the protoplasts were incubated with 100 μm ABA for 4 h. The values in each column are the mean of three independent replicates and the error bars indicate the sd.