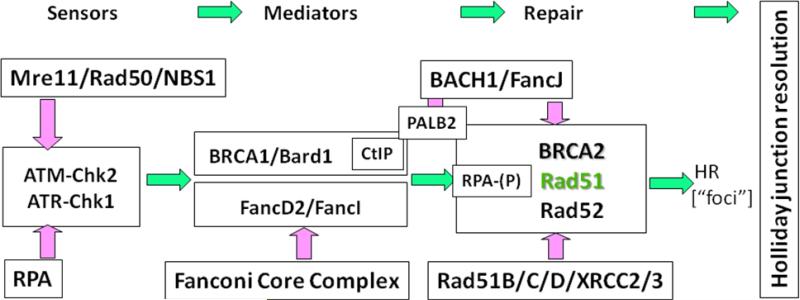
Figure 2.
The key proteins controlling homologous recombination. The main engine of HR is the Rad51 recombinase, which can often be observed by the formation of Rad51 foci in cells. Immediately upstream of Rad51 are BRCA2 and Rad52, which mediates the conversion of RPA-coated ssDNA into Rad51 filaments. The Rad51 paralogues (Rad51B/C/D, XRCC2/3) assist in this process in ways that still need to be defined. Between BRCA1 and BRCA2, there are a number of mediator proteins that support Rad51 function, such as BACH1, PALB2 and CtIP. The Fanconi Anemia proteins are playing a role in HR, particularly for collapsed replication forks in ways that still need to be determined. Upstream damage sensors send important signals to mediators of HR, such as Chk2-mediated phosphorylation of BRCA1. Any of the points in this pathway of HR are potentially targetable sites for enhancing the therapeutic effect of ionizing radiation.