Fig. 1. Schematic drawing of right proximal femur in bent lines.
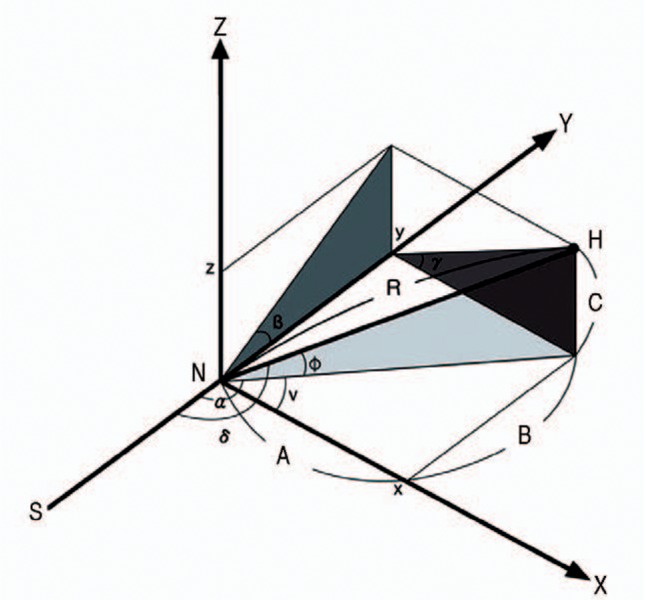
H: the center of the femoral head, N: the center of femoral neck at the base, S: the center of the femoral shaft, R: the length of the femoral neck (true head-neck distance), Y axis: the extension of the center of the femoral shaft, X axis: the vertical to Y axis in the frontal plane at the junction of femoral neck and the shaft, Z axis: the vertical to Y axis in the sagittal plane at the junction of femoral neck and the shaft.
So XY plane is frontal, YZ is sagittal, and XZ is transverse plane. The angle of femoral neck at XY, YZ and XZ plane has the value of α,β and γ respectively. Angle α is angle v plus 90, and angle v is valgus angle of femoral neck. Angle β is flexion angle and angle γ is anteversion angle of the femoral neck. The center of femoral head (H) is located in three-dimensional space and it has three coordinates of x, y, and z. A, B and C is the each value of x, y and z coordinate of the center of femoral head. Angle 'ϕ' is neck-frontal plane angle, and angle δ is true neck-shaft angle.
