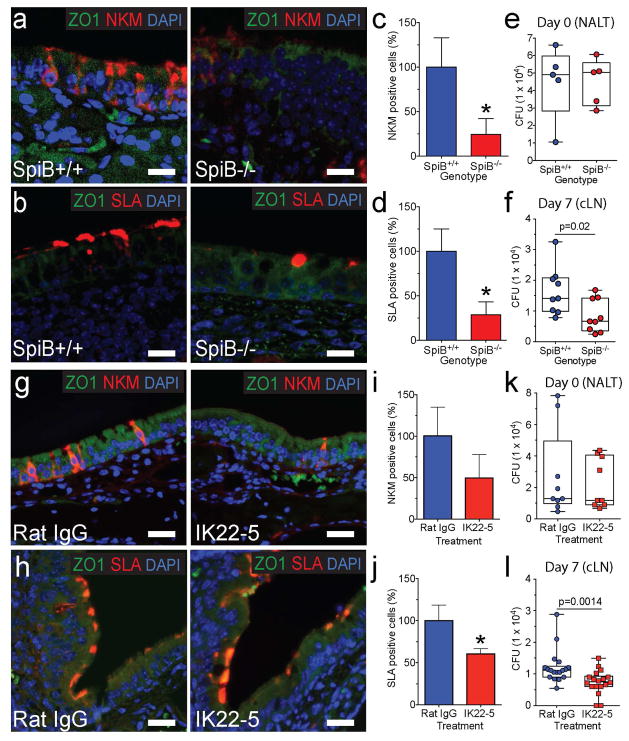
Fig. 1. Genetic and antibody-mediated loss of M-cells reduces Mtb translocation to cervical lymph nodes.
a,b, NALT from Spi-B+/+ (WT) and Spi-B−/− mice was stained with anti-ZO1 (cell marker) and NKM 16-2-4 (a, top) or anti-SLA (b, bottom). Scale bars are 20 μm. c, d, M-cells were quantified in the NALT of Spi-B+/+ and Spi-B−/− mice. The number of M-cells in WT mice was averaged and used to normalize percent positive cells for individual mice (n=3 mice/group). *p<0.05 compared to WT by Student’s t-test. e, f WT or Spi-B−/− mice were intranasally infected with Mtb and CFU determined in the NALT at day 0 (e) (n=5/group) and in LN at day 7 (f) (n=9/group). g, h NALT from control and IK22-5 treated BALB/c mice was stained with anti-ZO1 and NKM 16-2-4 (g, top) or anti-SLA (h, bottom). Scale bars are 20 μm. i, j M-cells were quantified in the NALT of wild-type and IK22-5 treated mice as above. *p<0.05 compared to WT by Student’s t-test. k, l Mice were intranasally infected with Mtb and CFU determined in the NALT at day 0 (k) (n=9/treatment) and in LN at day 7 (l) (n=18/treatment). Results are pooled from two independent infection experiments per mouse model. Statistical significance was determined by the Mann-Whitney U test.