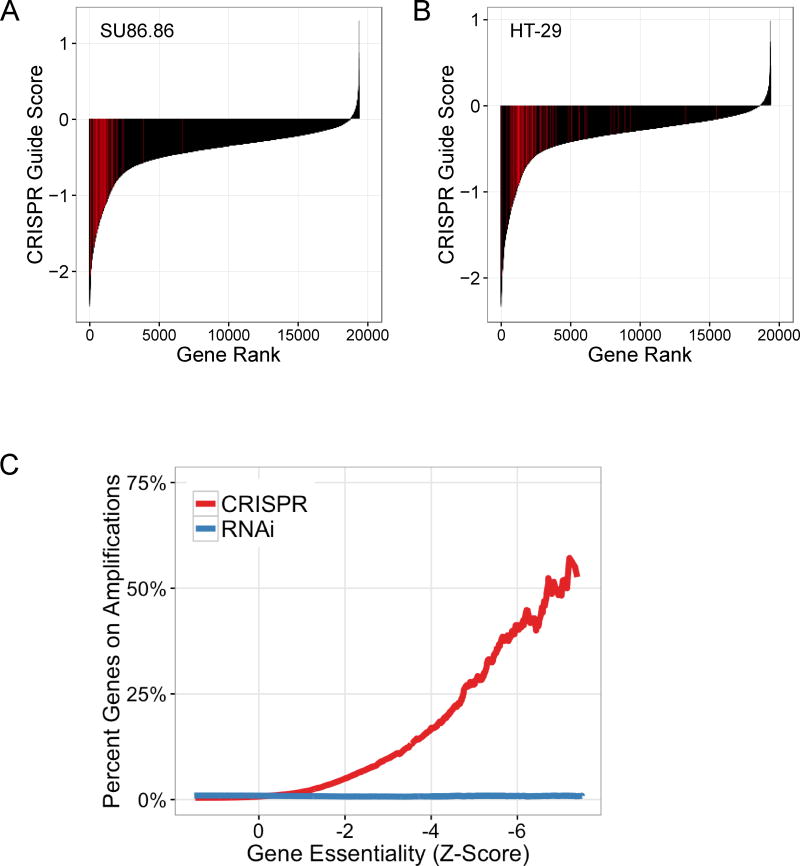
Figure 3.
Amplified genes represent the strongest perceived dependencies in pooled CRISPR-Cas9 screening data. (A, B) Rank ordered plots showing the second-best CRISPR-Cas9 guide score for each gene in the indicated cell lines. sgRNAs targeting genes within the amplicons represented in Figure 1 are highlighted in red for SU86.86 19q amplicon (A) and HT29 8q amplicon (B). These amplicon-targeting sgRNAs are significantly enriched as apparent dependencies relative to the other sgRNAs targeting genes outside these amplicons (one-sided Kolmogorov–Smirnov test: p = 1.04E-41, A; p = 5.57E-33, B). (C) The cumulative fraction of amplified genes at or below a given dependency score is shown for both CRISPR-Cas9 and RNAi pooled screening datasets. Amplified genes are defined as those genes with a copy number ratio > 2. Gene dependency scores are shown as global Z-scores for both CRISPR-Cas9 and RNAi screening datasets, with Z-scores representing standard deviations from the mean of all genes evaluated in all cell lines screened (CRISPR-Cas9, n = 33 cell lines; RNAi, n = 503 cell lines).