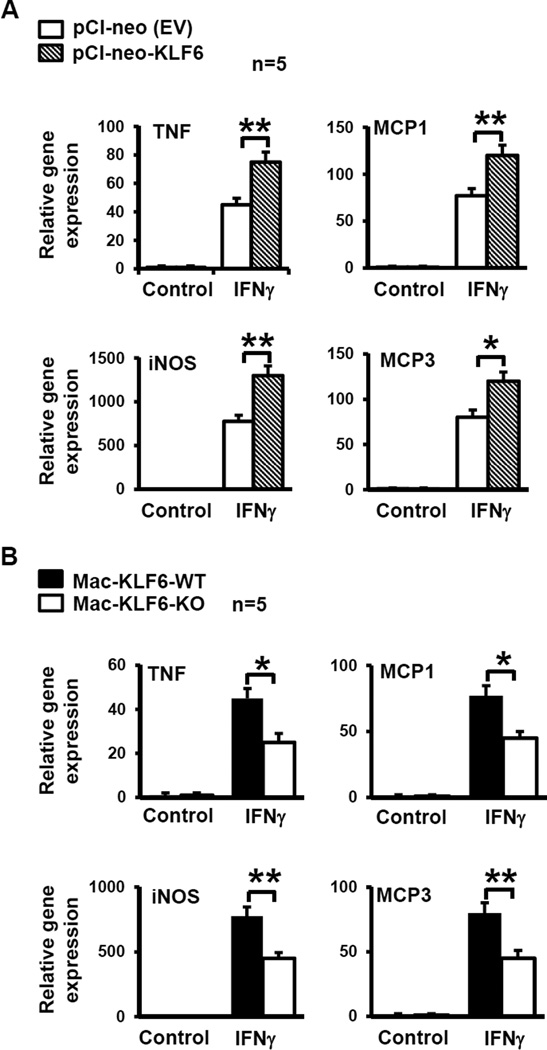
Figure 2. KLF6 induces pro-inflammatory gene expression in macrophages.
(A) Macrophages overexpressing KLF6 show enhanced expression of pro-inflammatory genes. RAW264.7 macrophages were transfected with pCl-neo (EV plasmid control) or pCl-KLF6 to overexpress KLF6. Cells were stimulated in vitro with PBS (control) or IFNγ (100U/ml) for 6hrs, then harvested for RNA isolation. cDNA was analyzed for expression of pro-inflammatory genes Tnf, Mcp1, inos, and Mcp3 by qPCR; *p≤0.02; **p≤0.003; n=5/group. (B) Macrophages deficient in KLF6 show reduced expression of pro-inflammatory genes. Peritoneal macrophages were isolated from Mac-KLF6-WT and Mac-KLF6-KO mice following thioglycolate elicitation. Cells were stimulated in vitro with PBS (control) or IFNγ (100U/ml) for 6hrs, then harvested for RNA isolation. cDNA was analyzed for expression of pro-inflammatory genes; *p≤0.03; **p≤0.001, n=5/group. All graphs show mean ± SEM.