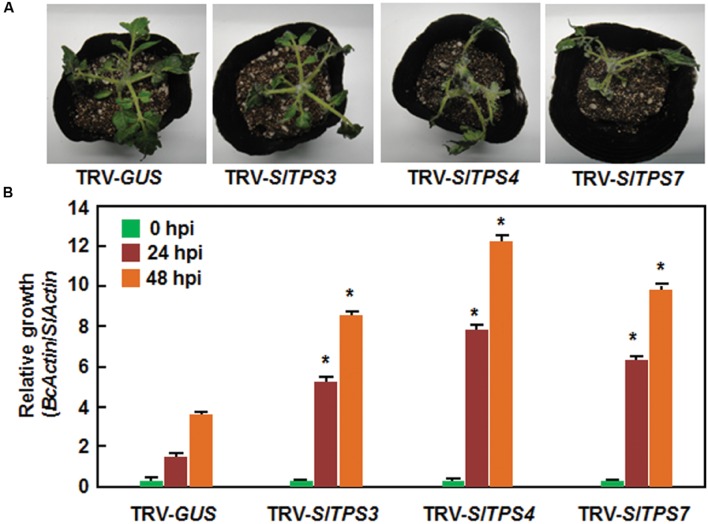
FIGURE 5.
Silencing of SlTPS3, SlTPS4, and SlTPS7 led to decreased resistance against B. cinerea in whole plant assays. (A) Disease phenotype of representative TRV-SlTPS3-, TRV-SlTPS4-, TRV-SlTPS7-, and TRV-GUS-infiltrated plants. Photos were taken at 4 days after inoculation. (B) In planta growth of B. cinerea in inoculated TRV-SlTPS3-, TRV-SlTPS4-, TRV-SlTPS7-, and TRV-GUS-infiltrated plants. Whole plant disease assays were done by foliar spraying with spore suspension at 4 weeks after VIGS infiltration. Transcript levels for B. cinerea BcActinA and tomato SlActin genes in B. cinerea-inoculated plants were analyzed using qRT-PCR and in planta relative growth of B. cinerea was shown as ratios of transcript levels of BcActinA/SlActin. Similar results were obtained in independent experiments (A) and data presented in (B) are the means ± SD from three independent experiments. ∗ above the columns indicate significant differences at p < 0.05 level between the TRV-SlTPS3/4/7-infiltrated and TRV-GUS-infiltrated plants.