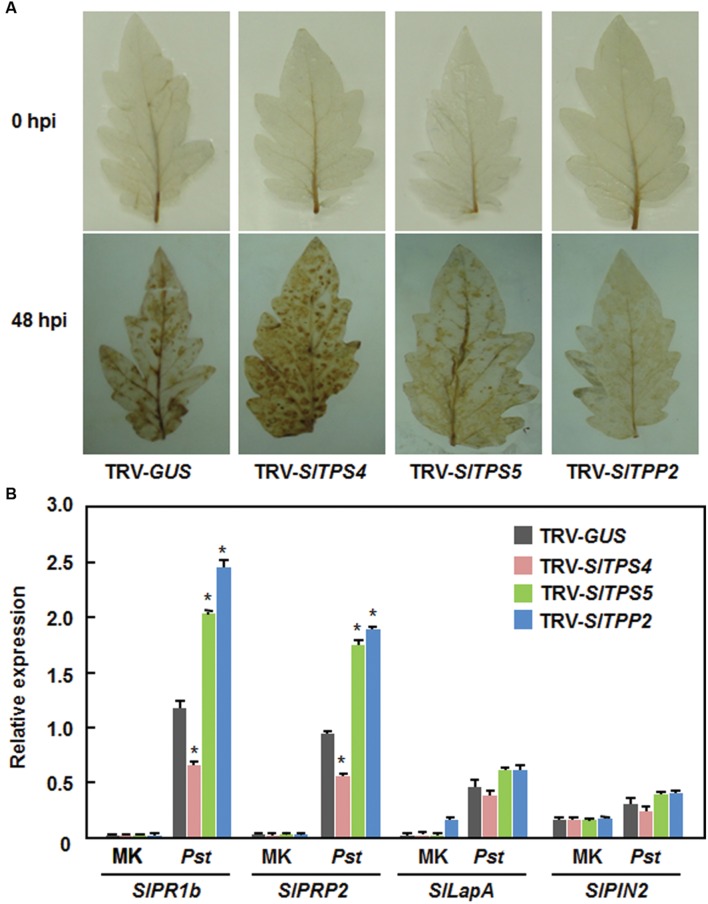
FIGURE 8.
Silencing of SlTPS4, SlTPS5, and SlTPP2 affected H2O2 accumulation and expression of SA signaling-responsive defense-related genes after infection with P. syringae pv. tomato DC3000. Whole plant disease assays were done by vacuum infiltration with suspension of P. syringae pv. tomato DC3000 at 4 weeks after VIGS infiltration and leaf samples were collected at 24 h after inoculation. (A) Accumulation of H2O2, as detected by DAB staining, in TRV-SlTPS4-, TRV-SlTPS5-, TRV-SlTPP2-, and TRV-GUS-infiltrated plants after infection of Pst D3000. (B) Expression patterns of selected defense-related genes in TRV-SlTPS4-, TRV-SlTPS5-, TRV-SlTPP2-, and TRV-GUS-infiltrated plants after infection of Pst DC3000. Expression data for the selected defense-related genes in TRV-SlTPS4-, TRV-SlTPS5-, TRV-SlTPP2-, and TRV-GUS-infiltrated plants were normalized with the value of a reference SlActin gene and relative expression levels were shown as folds of the SlActin expression level. Similar results were obtained in independent experiments (A) and data presented in (B) are the means ± SD from three independent experiments. ∗ above the columns indicate significant differences at p < 0.05 level between the TRV-SlTPS4/SlTPS5/SlTPP2-infiltrated and TRV-GUS-infiltrated plants.