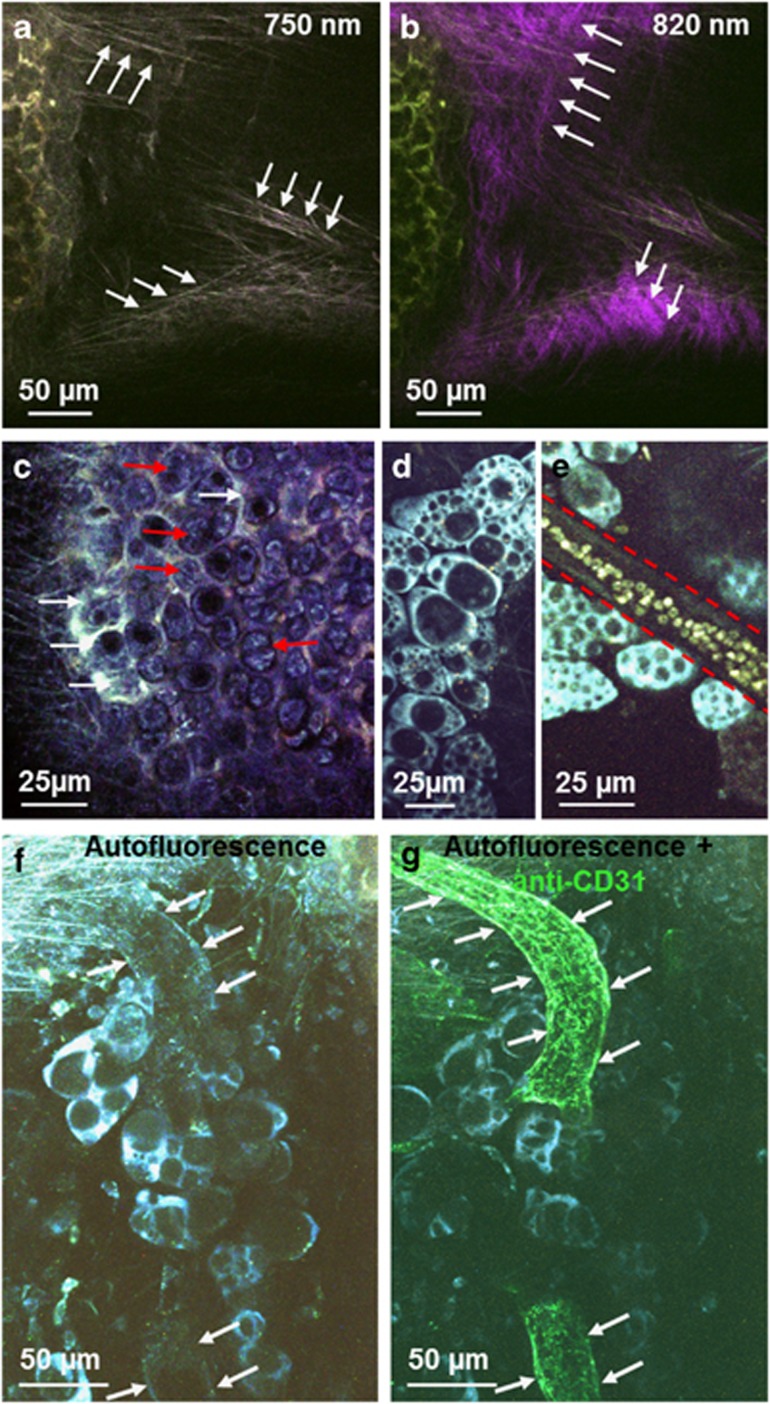
Figure 2.
Detailed morphology of the murine trachea ex vivo visualized by multiphoton microscopy. (a and b) Two types of fibers could be differentiated by using different excitation wavelengths. Elastic fibers were autofluorescent at an excitation wavelength of 750 nm (arrows in a), whereas collagen fibers exhibited second-harmonic generation signal at an excitation wavelength of 820 nm (arrows in b). (c) Detailed morphology of cartilage with chondrocytes (red arrows) and interterritorial matrix (white arrows). (d) Adipocytes could be identified by their non-fluorescent lipid droplets of various sizes in the brightly fluorescent cytoplasm. (e) Blood vessels could be identified by their weakly autofluorescent vessel wall (marked by dashed red line) with brightly fluorescent erythrocytes. (f and g) Blood vessels could be detected by a weak autofluorescence signal of the vessel wall (f, white arrows) and the same structure could be labeled by CD31 staining (g, white arrows).