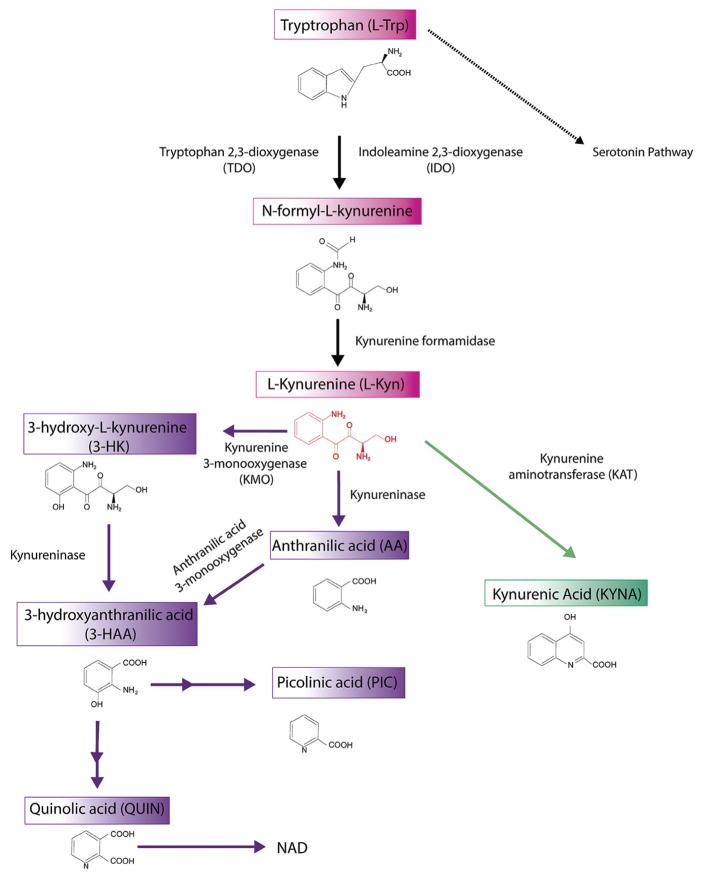
Fig. 2. The Kynurenine pathway of tryptophan degradation.
One of the main metabolic pathways of dietary L-tryptophan (L-Trp) in the brain is the kynurenine pathway (KP). The rate-limiting step of this pathway is the conversion of L-Trp to L-Kynurenine (L-Kyn) by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) and tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase (TDO). Through three pathways L-kynurenine is converted into kynurenic acid (KYNA), 3-hydroxykynurenine (3-HK) and anthranilic acid (ANA). The next step of the pathway is the conversion of 3-HK and ANA into 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid (3-HAA). 3-HAA, through several enzimatic reactions is converted into the final kynurenine pathway products picolinic acid (PIC) and quinolinic acid (QUIN). Finally, QUIN generates nicotinamide, and ultimately NAD+/NADP+