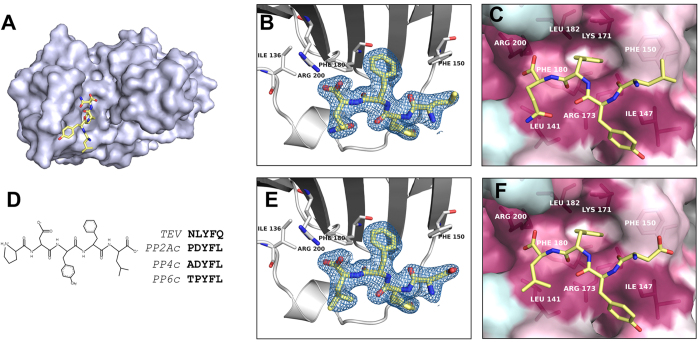
Figure 3. A conserved peptide binding site specifically recognizes the C-terminus of PP2Ac.
(A) Overview of the last four residues of the peptide generated after cleavage with the TEV protease (MGHHHHHHENLYFQ), LYFQ, bound to TIPRL (chain A). The peptide fragment is depicted as sticks over a surface representation of TIPRL, viewed from the bottom. (B) Close up view of the TEV site peptide LYFQ fitted into the electron density map (2Fobs–Fcalc) depicted at 1.0 σ. (C) Conservation pattern of the peptide binding site showing the LYFQ peptide in sticks representation. Consurf conservation scores mapped on the surface are colored as in Fig. 2 (burgundy: more conserved; turquoise: less conserved) and relevant amino acid side chains are labelled underneath the surface representation. (D) Sequence similarity between the TEV site peptide and the conserved C-terminus of type 2A phosphatases (PP2Ac, PP4c and PP6c). (E) The C-terminus of PP2Ac, DYFL, was fitted into the electron density map (2Fobs–Fcalc) of the LYFQ peptide depicted at 1.0 σ. (F) Same representation as Fig. 4C, showing the PP2Ac-derived peptide DYFL instead of TEV peptide.