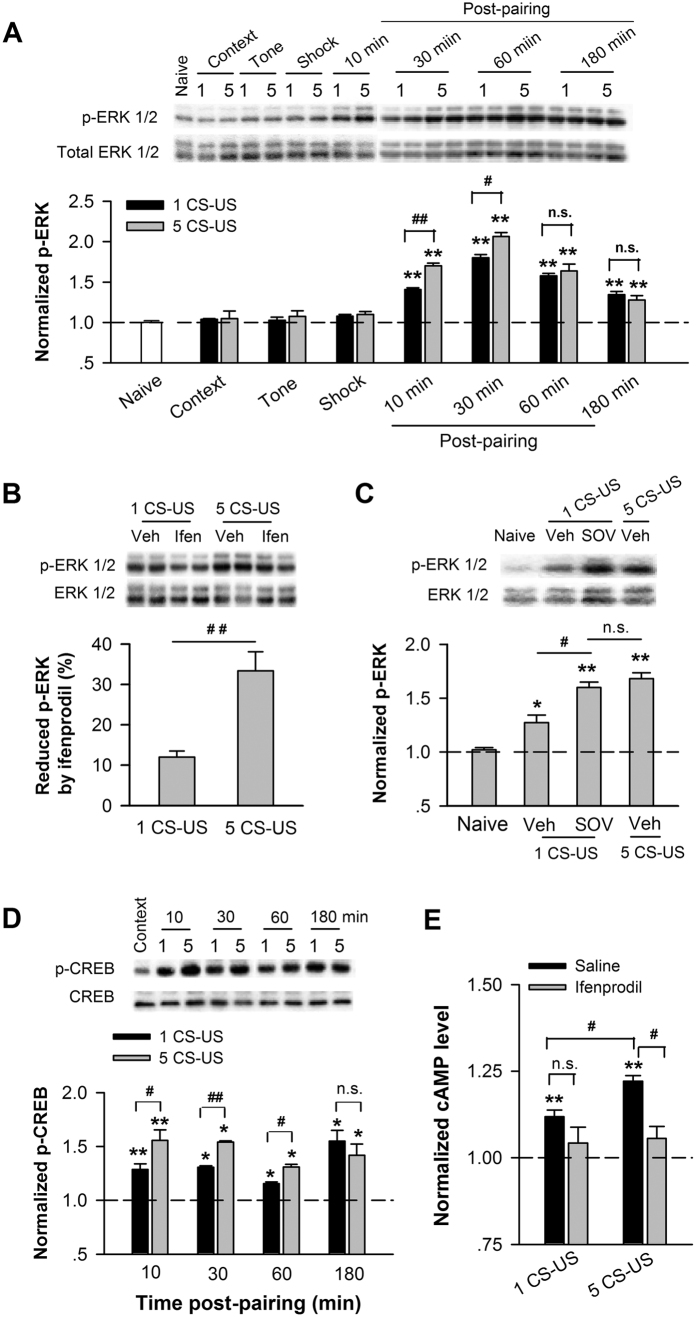
Figure 4. Increased amount of membrane GluN2B enhances the activity of the cAMP, ERK, and CREB signaling pathway in CA1 after fear conditioning.
Time course of ERK activation after fear conditioning. Immunoblots (upper) and quantification analysis (bottom) of ERK phosphorylation (p-ERK) in CA1 lysates taken from naïve, context alone, tone alone, shock alone, and conditioned rats, normalized to naïve rats. (B,C) Increased amount of membrane GluN2B enhances ERK activation. (B) Micro-injection of ifenprodil before training reduced ERK phosphorylation in area CA1. (C) Micro-injection of SOV before training with 1 CS-US increased ERK phosphorylation in CA1, normalized to vehicle-control or naïve rats. Top panels indicate the immunoblots. (D) Time course of CREB activation after fear conditioning. Immunoblots (top) and quantification analysis (bottom) of CREB phosphorylation (p-CREB) in CA1 lysates taken from unconditioned and conditioned rats, normalized to unconditioned context-control rats. (E) Effect of ifenprodil on the cAMP level in the CA1 region after fear conditioning. Quantification analysis of cAMP concentration in CA1 lysates extracted from unconditioned rats with infusion of saline (context) and conditioned rats with intra-CA1 infusion of saline versus ifenprodil before training, normalized to context-control rats. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 vs. control, #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01.