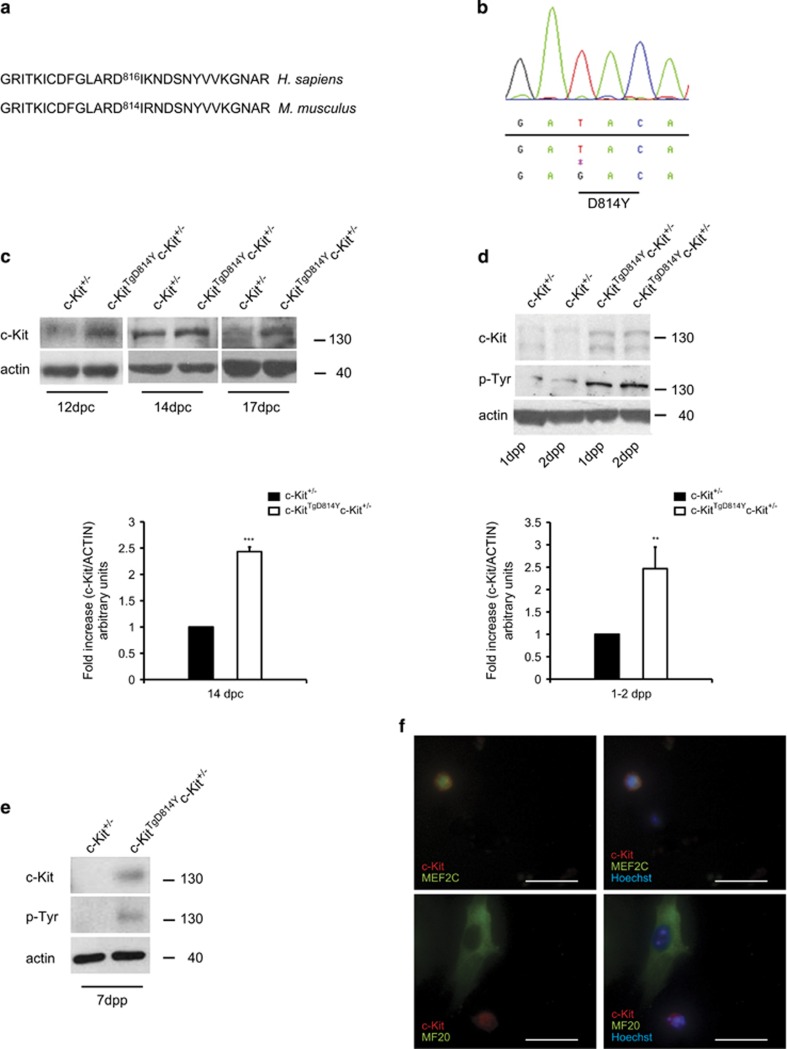
Figure 1.
D814Y substitution induces a constitutive c-Kit activation. (a) Pairwise local alignments of human (Homo sapiens) and mouse (Mus musculus) c-Kit protein sequences surrounding the putative residue for constitutive activation in the second kinase domain of the receptor. (b) Sequence chromatogram showing the aspartic acid to tyrosine mutation introduced in c-Kit mouse BAC RP23- 309C11. (c) WB and densitometry of c-Kit expression on hearts collected from embryos at different stages of development. Mutant c-Kit protein is expressed 2.5-fold higher than endogenous level in c-KitTgD814Yc-Kit+/− embryos. (d) WB and densitometry of c-Kit expression on total heart lysate collected from neonatal mice. Mutant c-Kit protein is expressed 2.5-fold higher than endogenous c-Kit protein levels in c-KitTgD814Yc-Kit+/− mice. c-Kit activation is shown by a pan phospho-tyrosine antibody that recognizes a specific band at the receptor height. (e) WB analysis on hearts collected from 7 dpp mice. Data are obtained from at least three separate hearts and reported±S.D.; **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. (f) Immunofluorescence analysis of c-Kit+ cells (red) in isolated c-KitTgD814Y neonatal myocytes cultured for 24 h co-stained with MEF2C (green) and MF20 (green). Nuclei (blue) were counterstained with Hoechst 33342. Scale bars 30 μm