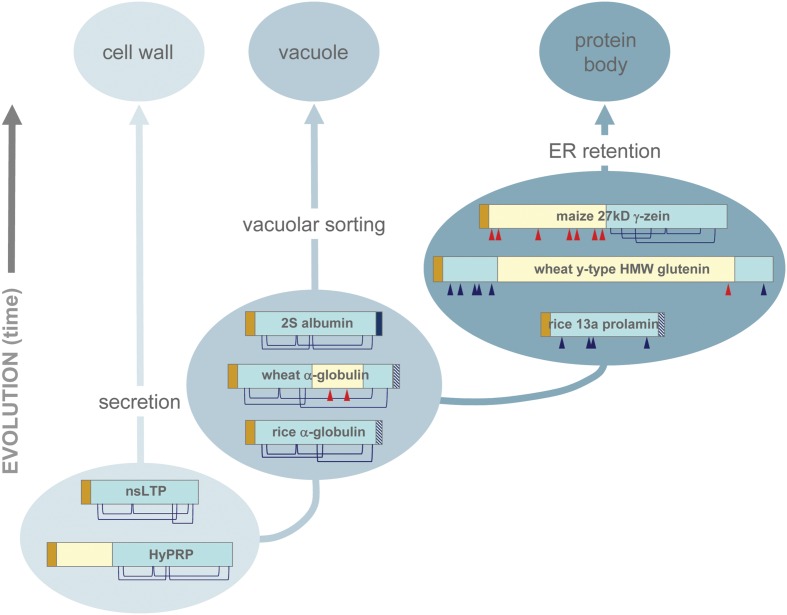
FIGURE 1.
A model of the evolutionary events at the origin of protein bodies. The model describes the origin of prolamins that are self-sufficient for PB formation and probably have a dominant effect on those that evolved later. Proteins with 8CM motifs are secreted or sorted to the vacuole, depending on the presence or not of vacuolar sorting signals. Insertions that do not alter the disulphide bonds of the 8CM motif do not affect protein destiny. Extensive polymerization that leads to PB formation can result from insertions that inhibit the correct formation of the four intra-chain bonds, deletions that involve the loss of critical Cys residues, or additions of domains containing new Cys residues. The repetitive domains may also mediate interactions with the ER membrane. Vacuolar sorting signals may be present or absent in PB proteins, but PB formation has anyway a dominant effect on intracellular traffic. Phylogenetic analysis and the results of protein engineering and expression of individual genes indicate that the PB forming prolamins evolved from superfamily members that are sorted to the vacuole, not from secreted members. The schematic protein structures are based on the following GenBank accessions: EU968356.1 (maize nsLTP), EU964401.1 (maize HyPRP), CAA40015.1 (2S albumin), ABG68034.1 (wheat α-globulin), BAA09308.1 (rice α-globulin), 27 kD zein, ABG68035.1 (wheat y-type HMW glutenin), and BAA36697.1 (rice 13a prolamin). Brown: signal peptide; light blue: conserved 8CM motif, or portions of it; yellow: Pro-rich or Glu-rich domain; blue: vacuolar sorting sequence; striped blue: putative vacuolar sorting sequence; blue lines: intra-chain disulphide bonds of the 8CM motif; blue triangles: Cys residues originating from the 8CM motif; red triangle: Cys residues that do not originate from the 8CM motif.