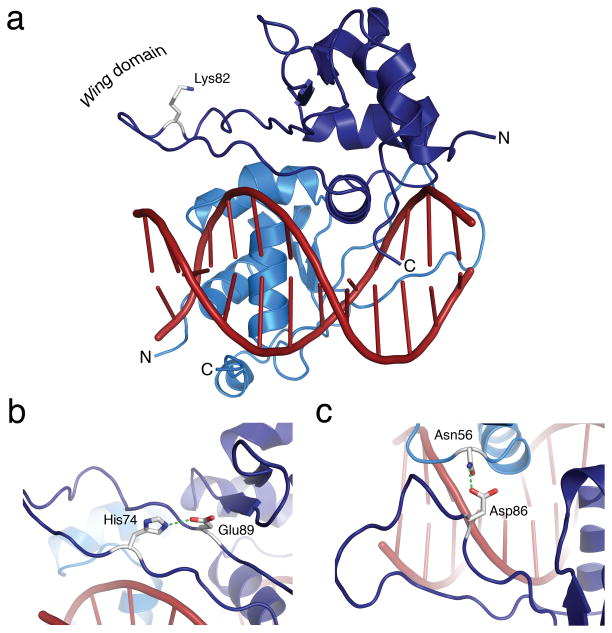
Figure 2. The HSF2 wing domain is solvent exposed and does not contact DNA.
a) Side view of the HSF2 DBD with the wing domain indicated on the left and the recognition helix inserted into the major groove of the HSE DNA site. Lys82, depicted as a stick model, is directed away from the DNA and exposed for modification. b) His74 and Glu89 form a hydrogen bond that acts as a wedge to pry open the wing domain. c) Asp86 engages Asn56 from the adjacent monomer to form a hydrogen bond that is predicted to strengthen the dimer interface and anchor the wing domain.