Fig. 3.
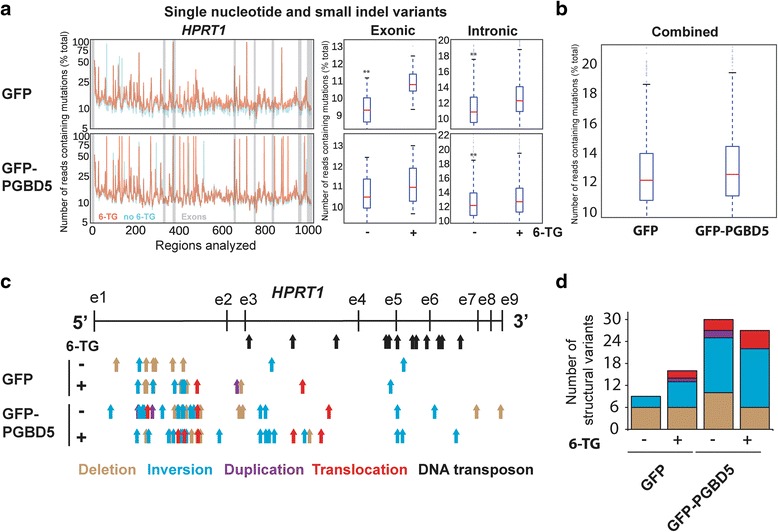
Comprehensive genomic analysis of HPRT1 mutations reveals PGBD5-mediated induction of complex genomic rearrangements. a (left) Distribution of the mutational frequency (y-axis) and the location (x-axis) of single nucleotide variants (SNV) and small indels in HPRT1 of cells before (blue) and after (orange) thioguanine resistance selection. Exons are denoted by gray bars. (right) Comparative analysis of the frequencies of SNVs and indels in HPRT1 before (−) and after (+) thioguanine resistance selection reveals no significant differences between GFP and GFP-PGBD5 expressing cells; * and ** denote p < 0.05 and p < 0.01 for exonic and intronic variants, respectively (Exonic GFP p = 8.32e-6, exonic GFP-PGBD5 p = 0.09, intronic GFP p = 2.77e-36, intronic GFP-PGBD5 p = 4.77e-06). b Combined comparative analysis of the frequencies of SNVs and indels in HPRT1 in GFP and GFP-PGBD5 expressing cells (p = 7.90e-4). c Distribution of the locations of the 5′ ends of complex structural variants in cells before (−) and after (+) thioguanine resistance selection, as detected by laSV and marked by arrows denoting deletions (brown), inversions (blue), duplications (purple), and translocations (red). Black arrows mark annotated DNA transposons. d Expression of GFP-PGBD5 leads to induction of complex structural variants before (−) and after (+) thioguanine resistance selection (Total number of SVs GFP vs. PGBD5, p = 0.001, Poisson test, 95 % confidence interval 0.262–0.713)
