Figure 1.
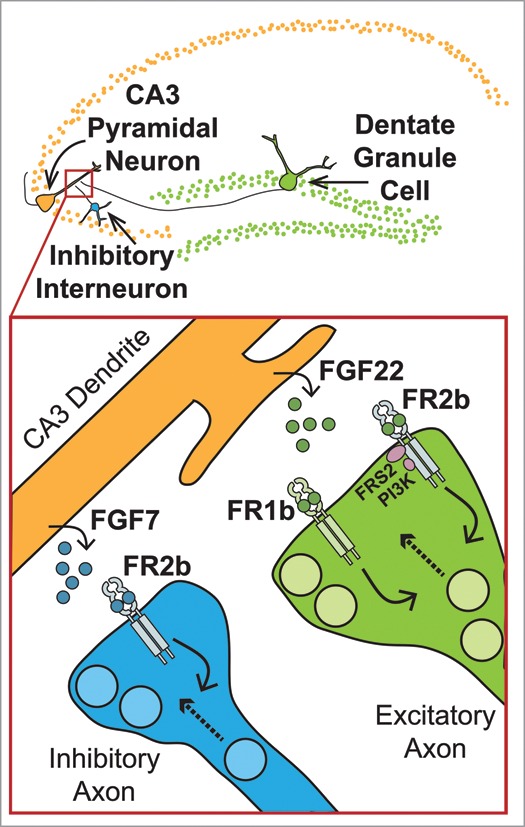
Target-derived FGFs induce excitatory and inhibitory presynaptic differentiation. Top: In the hippocampal circuit, dentate granule cells (DGCs) provide a major excitatory input to the CA3, and interneurons provide the inhibitory input. Bottom: FGF22 and FGF7 are secreted at excitatory and inhibitory nascent synapses on CA3 dendrites in the hippocampus.14,17 FGF22 acts on FGFR2b and FGFR1b within DGCs to induce synaptic vesicle accumulation in excitatory axon terminals, and FGF7 acts on FGFR2b within interneurons to induce synaptic vesicle accumulation within inhibitory axoN-terminals.1,14 FGFR2b activated by FGF22 utilizes kinase activity and signaling downstream of FRS2 and PI3K, but not PLC-gamma, to induce accumulation of excitatory synaptic vesicles.1
