Fig. 1.
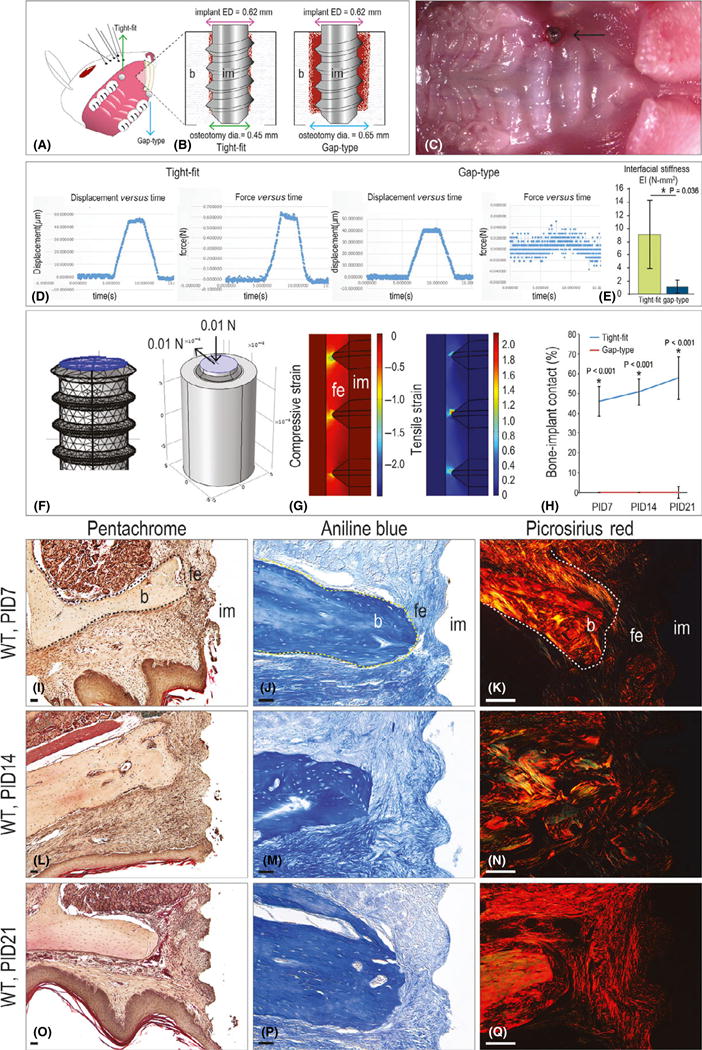
A model of fibrous encapsulation and implant failure. (A) Schematic of the implant insertion site in the mouse oral cavity and (B) of the tight-fit and gap-type interfaces. (C) Intra-oral photograph of the implant, immediately after placement. (D) Representative displacement (μm) versus time (sec), and force (N) versus time (s), collected from tight-fit and gap-type implants. (E) Interfacial stiffness (represented by EI values) of tight-fit and gap-type interfaces. (F) Three-dimensional finite element model of gap-type implants. (G) Principal compressive strain and principal tensile strain in the gap-type interface. (H) Quantification of %BIC in tight-fit (blue) and gap-type (red) implants at the time points indicated. (I) Representative sagittal tissue sections from implants with gap-type interfaces analysed on PID7 (N = 12), (L) 14 (N = 12) and (O) 21 (N = 12). (J) Representative sagittal tissue sections stained with aniline blue to detect osteoid matrix on PID7 (N = 12), (M) 14 (N = 12) and (P) 21 (N = 12). (K) Representative sagittal tissue sections stained with picrosirius red to detect collagen organization on PID7 (N = 12), (N) 14 (N = 12) and (Q) 21 (N = 12). Abbreviations: BIC, bone-implant contact; b, bone; dia, diameter; ED, external diameter; fe, fibrous envelope; im, implant; PID, post-implant day; WT, wild-type. Scale bar = 50 μm for all panels.
