Fig. 2.
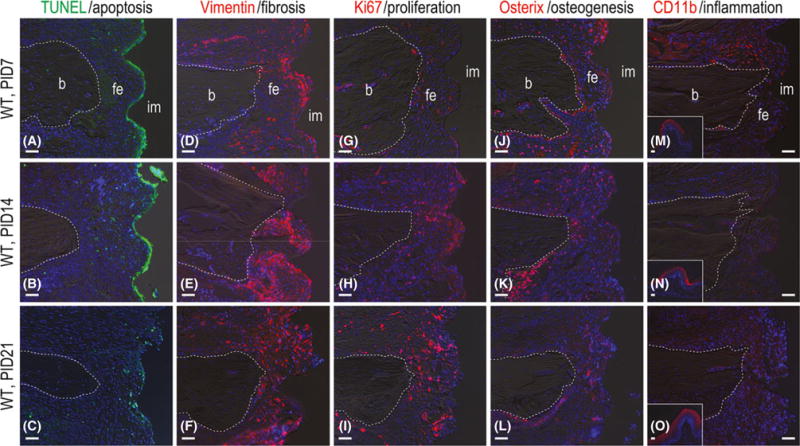
Fibrous encapsulation of gap-type implants is terminal. (A) Representative sagittal tissue sections stained to detect cell nuclei (DAPI, blue) and cells undergoing apoptosis (TUNEL, green) on PID7 (N = 12), (B) 14 (N = 12) and (C) 21 (N = 12). (D) Immunostaining with Vimentin to detect fibroblasts on PID7 (N = 12), (E) 14 (N = 12) and (F) 21 (N = 12). (G) Immunostaining with Ki67 to detect cell proliferation on PID7 (N = 12), (H) 14 (N = 12), and (I) 21 (N = 12). (J) Immunostaining with Osterix to detect pre-osteoblasts on PID7 (N = 12), (K) 14 (N = 12) and (L) 21 (N = 12). (M) Immunostaining with CD11b to detect monocyte/macrophage on PID7 (N = 12), (N) 14 (N = 12) and (O) 21 (N = 12). Abbreviations: b, bone; CD11b, cluster of differentiation molecule 11b; fe, fibrous envelope; im, implant; PID, post-implant day; TUNEL, terminal deoxynucleotidyl Transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labelling; WT, wild-type. Scale bar = 50 μm for all panels.
